Ubiquitination pathway
The ubiquitination pathway has been implicated in a number of genetic disorders and diseases including cancer and neurological diseases which result from the build-up of protein aggregates such as; Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and Huntingdon’s disease. This collection has been generated in close collaboration with Prof. Steve Jackson (Gurdon Institute, Cambridge, United Kingdom).
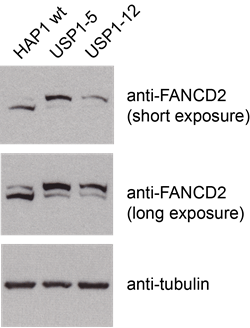
Deubiquitination of FANCD2 by USP1 is impacted in a USP1 knockout cell lines.
Cells were washed with PBS, lysed in Frackelton buffer (10 mM Tris/HCl pH 7.5, 50 mM NaCl, 30 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 1 % Triton X-100, 50 mM NaF and protease inhibitors).
They were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using anti-FANCD2 (sc-20022 from Santa Cruz). HAP1 wild-type cells were compared to cells bearing a frameshift mutation in USP1.
Explore our popular knockout cell lines for deubiquitinating enzymes genes
Order products
Human knockout HAP-1 cells
The single largest bank of isogenic cell lines with over 7,500 cell lines to choose from and trusted by academia, biotech, and pharma research labs.
Cancer-related cell lines
Choose from over 300 knock-in and knockout cell line models in many standard cancer cell lines such as DLD1, MCF10A, and HCT116.
Cas9 Stable Cell Lines
Simplify gene editing experiments with stably expressing Cas9 cell lines
CRISPRmod CRISPRa dCas9-VPR Stable Cell Lines
Streamline CRISPR activation experiments with stably expressing dCas9-VPR cell lines
Helpful Resources
Cell Line Engineering Brochure
Save time and de-risk your project. With 7,500 readymade knockouts from Horizon you can validate your research without having to invest valuable time, money, and resources.
Learn more
Top peer reviewed scientific articles using HAP1 cell lines
Need help?
Can't find the right cell model for your research?
Our Express and Custom engineering services could help you.
