Pathways sumoylation trans
SUMOylation is a reversible post-translational modification involved in transcription
Pathways sumoylation trans
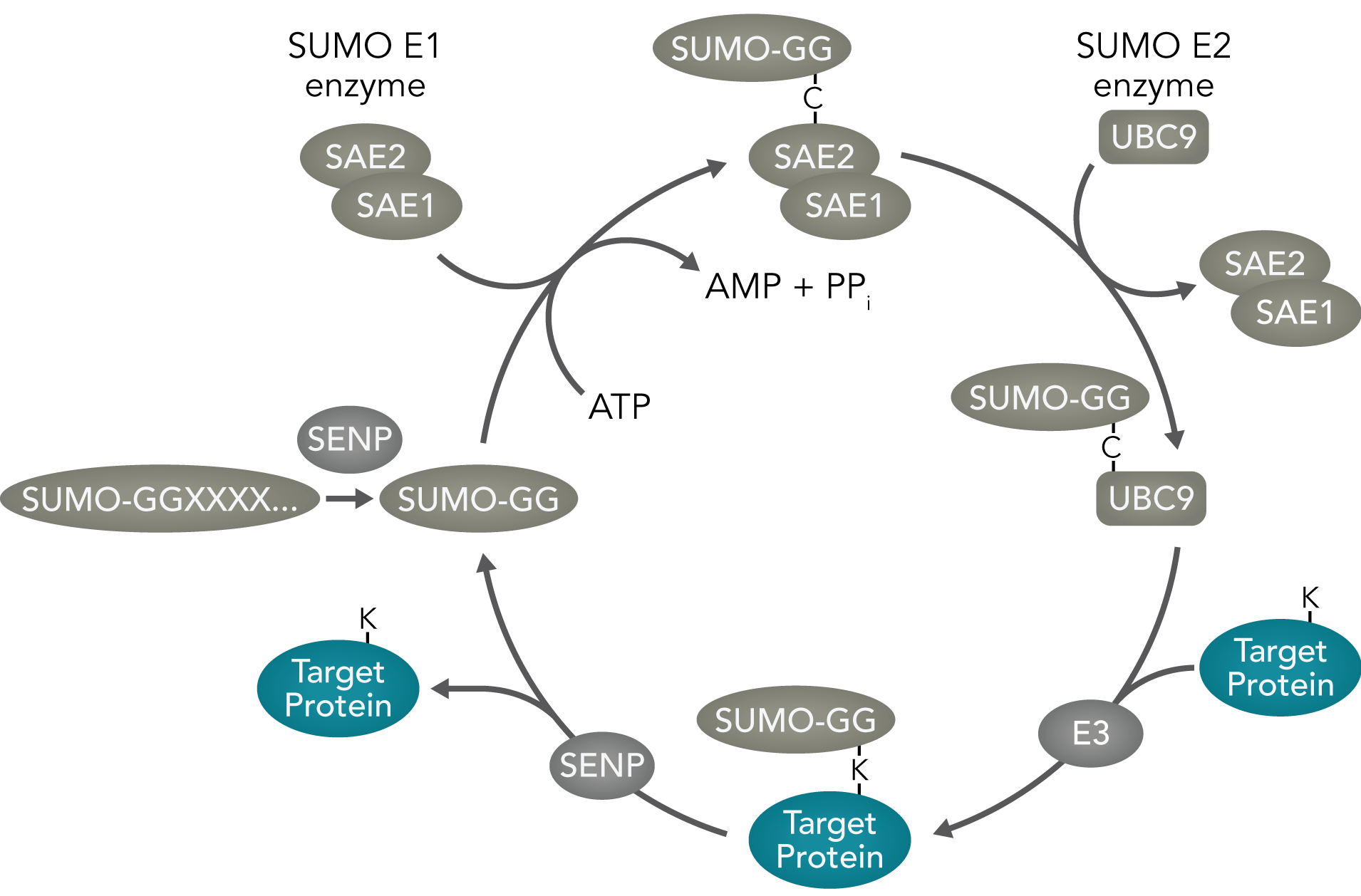
SUMOylation is a reversible post-translational modification involved in transcription, DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, splicing, assembly of ribosomes and many other cellular processes. SUMO (small ubiquitin-like modifier) is attached as a monomer or polymer through a process akin to that of ubiquitination. It is attached via the sequential action of E1, E2 and E3 enzymes, and can be removed by SUMO1/Sentrin-specific proteases SENPs).
To support your research on the role and mechanism of SUMO modifications, Horizon has developed a collection of human knockout HAP1 cell lines that lack components of the SUMOylation pathway. These knockouts enable study of pathway redundancy, identification of subcellular function and characterization of the proteins themselves by providing a clean background in which mutants can be expressed.
Explore our popular knockout cell lines for SUMOylation
| ARHGAP31 | SENP1 | SENP2 | SENP3 |
| SENP5 | SUMO1 | SUMO3 |
Order products
Human knockout HAP-1 cells
The single largest bank of isogenic cell lines with over 7,500 cell lines to choose from and trusted by academia, biotech, and pharma research labs.
Cancer-related cell lines
Choose from over 300 knock-in and knockout cell line models in many standard cancer cell lines such as DLD1, MCF10A, and HCT116.
Cas9 Stable Cell Lines
Simplify gene editing experiments with stably expressing Cas9 cell lines
CRISPRmod CRISPRa dCas9-VPR Stable Cell Lines
Streamline CRISPR activation experiments with stably expressing dCas9-VPR cell lines
