Phosphatases in disease
Many phosphatases are key in the development of pathological pathways where inhibition can reverse or delay the onset of human diseases.
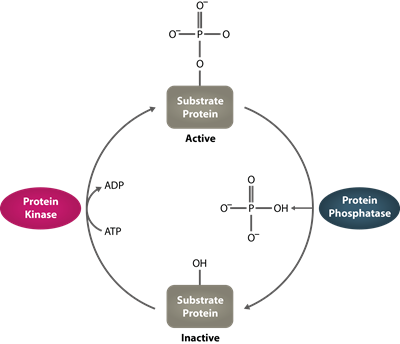
Abnormal serine/threonine phosphatase activity has been linked with several diseases, including diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, cancer, and Alzheimer's disease. Therefore, the pharmacological manipulation of phosphatase activity is an attractive strategy for the treatment of such conditions.
Serine/Theonine phosphatases are metal-requiring enzymes that regulate many pathways involved in cell proliferation, programmed cell death (apoptosis), embryonic development, and cell differentiation. They are grouped into two gene families - the PPP and the PPM gene families, based on sequence analysis.
PPP Gene family
The PP1 subfamily is comprised of a catalytic subunit that interacts with several proteins including targeting subunits and inhibitor proteins.
The PP2A subfamily are heterotrimers comprised of a catalytic subunit and two regulatory subunits.
PPM Gene Family
This group corresponds to the PP2C enzymes, which are activated by high concentrations of magnesium. This subfamily is less well-studied than the PPP group, and little is known about their regulation.
Explore our popular knockout cell lines for studying Serine-threonine Phosphatase
Order products
Human knockout HAP-1 cells
The single largest bank of isogenic cell lines with over 7,500 cell lines to choose from and trusted by academia, biotech, and pharma research labs.
Cancer-related cell lines
Choose from over 300 knock-in and knockout cell line models in many standard cancer cell lines such as DLD1, MCF10A, and HCT116.
Cas9 Stable Cell Lines
Simplify gene editing experiments with stably expressing Cas9 cell lines
CRISPRmod CRISPRa dCas9-VPR Stable Cell Lines
Streamline CRISPR activation experiments with stably expressing dCas9-VPR cell lines
