- Non-mammalian research tools
- Yeast Knockout
Yeast Knockout

Yeast Knockout
1Start Here
2Choose
Developed by the Saccharomyces Genome Deletion Project, the Yeast Knockout (YKO) Collection includes knock-out strains covering 96% of the yeast genome. The inclusion of distinct tags - or "molecular barcodes" - that identify each strain allows phenotypic analysis to be performed on a single gene basis or a genome-wide scale. By using the yeast knock out strains for functional profiling, one can also gather much information about human gene function by analogy.
Features
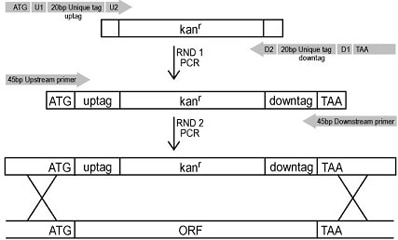
The yeast knock out strains were systematically created using a PCR-based strategy. By means of two sequential PCR reactions - the first to incorporate the appropriate tags and confer the antibiotic resistance gene and the second to incorporate the mitotic recombination sites - each ORF was replaced with a KanMX cassette using homologous recombination. Each cassette contains a unique 20 base pair nucleotide sequence of DNA known as a "molecular barcode" allowing for parallel analysis. Also incorporated is a common set of flanking DNA tag sequences allowing amplification of the unique tags.
Highlights
- 6,000 individual genes are represented in four backgrounds (haploids of MATa and MATalpha, heterozygous diploid, and homozygous diploid), thereby creating over 20,000 distinct knock out strains
- Molecular barcodes allow for parallel analysis of gene function
- The mutant yeast strains can also be analyzed individually via sequencing or by using a whole genome approach
| Strain | Background | Genotype |
|---|---|---|
| MATa | BY4730 | MATa leu2Δ0 met15Δ0 ura3Δ0 |
| MATalpha | BY4739 | MATalpha leu2Δ0 lys2Δ0 ura3Δ0 |
| MATa | BY4741 | MATa his3Δ1 leu2Δ0 met15Δ0 ura3Δ0 |
| MATalpha | BY4742 | MATalpha his3Δ1 leu2Δ0 lys2Δ0 ura3Δ0 |
| Het/Hom Dip | BY4743 | 4741/4742 |
| Homozygous diploids are in the BY4743 background unless 4730/4739 is indicated | ||
A wealth of information - including genetic and physical maps along with DNA sequence information - is available from the Saccharomyces Genome Database (SGD) at Stanford University.
Note
We provide certain clone resources developed by leading academic laboratories. Many of these resources address the needs of specialized research communities not served by other commercial entities. In order to provide these as a public resource, we depend on the contributing academic laboratories for quality control.
Therefore, these are distributed in the format provided by the contributing institution "as is" with no additional product validation or guarantee. We are not responsible for any errors or performance issues. Additional information can be found in the product manual as well as in associated published articles (if available). Alternatively, the source academic institution can be contacted directly for troubleshooting.
Individual yeast knock out strains are provided as a live culture in a 2 mL tube. Each tube contains YPD broth with G418 (200 µg/mL) and is supplemented with 15% glycerol. Within 3 to 4 days of receiving your order, we will ship your clone at room temperature via express delivery. Store the stock clone at 4°C for up to one week or -80°C indefinitely.
The Yeast Knock Out collections are available as frozen glycerol stocks in 96-well plates. The glycerol stocks are a culture of the Yeast Knock Out in YPD media and glycerol. These plates ship on dry ice and can be maintained indefinitely at -80°C.
- E. A. Winzeler et al., Functional characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome by gene deletion and parallel analysis. Science. 285(5429), 901-906 (6 August 1999).
- G. Giaever et al., Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature. 418, 387-391 (2002).
- A. Wach, A. Brachat, R. Poehlmann, P. Philippsen, New heterologous modules for classical or PCR-based gene disruptions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 10(13), 1793-1808 (December 1994).
