Edit-R synthetic crRNA negative controls
Bioinformatically designed to not target any gene in human or mouse genomes
Synthetic guide RNAs for efficient gene knockout & unparalleled specificity
- Transfection-ready RNAs eliminate cloning and in vitro transcription steps
- Chemically modified for improved nuclease resistance
Reminder: Synthetic crRNA must be paired with synthetic tracrRNA to form the full guide RNA complex that targets Cas9 editing.

AAVS1/Rosa26 cutting controls are designed to target regions of the genome that do not result in functional knockout of a protein or known phenotypic changes. These regions are sometimes known as safe harbor regions. These guides are validated for mismatch detection assays and are recommended for screening applications as an additional control that results in Cas9 cutting without a phenotypic readout.
Non-targeting Controls are recommended as negative controls for experiments using crRNAs in human or mouse cells. All Edit-R Non-targeting Controls are designed to have a minimum of three mismatches or gaps to all potential PAM-adjacent targets in human and mouse genomes. Changes in viability or gene expression levels in cells treated with these controls likely reflect a baseline cellular response that can be compared to the levels in cells treated with target-specific crRNAs.
Remember to order tracrRNA for use with your controls!
Edit-R CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Engineering Platform
The Dharmacon Edit-R Gene Engineering platform is based on the Type II CRISPR-Cas9 system from the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes which can be engineered and adapted to edit genes in mammalian cells. When Cas9, the endonuclease component of a CRISPR-Cas system, is complexed with two RNAs called the CRISPR RNA (crRNA) and the trans-activating crRNA (tracrRNA), it forms a complex that cleaves DNA. This flexible system can be exploited to induce site-specific genome modifications to program, regulate and precisely interrogate gene function.
The Dharmacon Edit-R CRISPR-Cas9 platform includes the three critical components required for gene editing in mammalian cells, based on the natural S. pyogenes system:
- A protein, mRNA, or lentiviral vector expressing a mammalian codon-optimized gene sequence encoding Cas9 nuclease
- A chemically synthesized trans-activating CRISPR RNA (tracrRNA), and
- A chemically synthesized CRISPR RNA (crRNA) designed to the gene target site of interest
How much crRNA & tracrRNA do I need?
This table provides the approximate number of experiments that can be carried out for lipid transfection methods at the recommended crRNA:tracrRNA working concentration (25 nM:25nM) in various plate/well formats. Calculations do not account for pipetting errors.| crRNA nmol | tracrRNA nmol | 96-well plate 100 µL reaction volume | 24-well plate 500 µL reaction volume | 12-well plate 1000 µL reaction volume | 6-well plate 2500 µL reaction volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 | 800 | 160 | 80 | 32 |
| 5 | 5 | 2000 | 400 | 200 | 80 |
| 10 | 10 | 4000 | 800 | 400 | 160 |
| 20 | 20 | 8000 | 1600 | 800 | 320 |
The Edit-R predesigned guide RNA guarantee
We guarantee that EVERY predesigned guide RNA will provide successful editing at the target site when delivered as described in the Edit-R Technical Manuals.
The Edit-R guide RNA guarantee is valid when used with any wild type S. pyogenes Cas9 nuclease, including mRNA, expression plasmid, protein, or stable Cas9 expression, and Edit-R crRNAs must be used with Edit-R tracrRNA for the guarantee to apply.
Analysis of editing of the treated cell population must be shown using a T7EI or Surveyor mismatch detection assay. If successful editing is not observed for a predesigned Edit-R guide RNA while an appropriate side-by-side Edit-R positive control is successful, a one-time replacement of a different predesigned Edit-R guide RNA of the same format and quantity will be provided at no cost.
A replacement will only be approved upon discussion with our Scientific Support team.
Successful editing at the DNA level does not always lead to functional gene knockout; it is recommended to test multiple guide RNAs to determine the most effective guide RNA for knockout of your target gene.
This guarantee does not extend to any accompanying experimental costs, does not apply to guide RNAs ordered via the CRISPR Design Tool, and will not be extended to the replacement guide RNA.
High percentage of gene editing using the T7E1 assay to determine indel formation of the Edit-R AAVS1 cutting controls

Jurkat cells (250,000/96w) were nucleofected with (SE buffer, program CL-120) 50 pmol of RNP (40 µM NLS-Cas9 + 80 µM sgRNA) in triplicate. U2OS cells hEF1α-Cas9 were transfected using 0.15 µL Dharmafect 4/96w + 50 µM sgRNA (incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes in MEM solution).
After 72 hours cells were harvested for direct lysis (+ Rnase + proteinase K). Primers per spacer region were used to amplify 450-800 bp genomic amplicon from the edited and unedited samples. A hot-start Phusion II touch-down PCR program was used to generate amplicons for each sample (Tm ~65 for each). PCRs were directly incubated with T7 endonuclease I and ran on a 2% agarose SyberSafe gel @ 80V for 90 minutes.
TIDE analysis confirms high efficiency of indel formation using Edit-R AAVS1 cutting control guides

Jurkat cells (250,000/96w) were nucleofected with 50 pmol of RNP (40 µM NLS-Cas9 + 80 µM sgRNA) in SE buffer and program CL-120, in triplicate. U2OS cells were transfected using 0.15 µL Dharmafect 4/96w + 50 µM sgRNA (incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes in MEM solution).
After 72 hours cells were harvested for direct lysis. Primers per spacer region were used to amplify 450-800 bp genomic amplicon from the edited and unedited samples. A hot-start Phusion II touch-down PCR program was used to generate amplicons for each sample. PCRs were sent for Sanger sequencing. Sequencing files were analyzed by tracking of indels by decomposition (TIDE).
Efficient CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing achieved with synthetic sgRNA and synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA
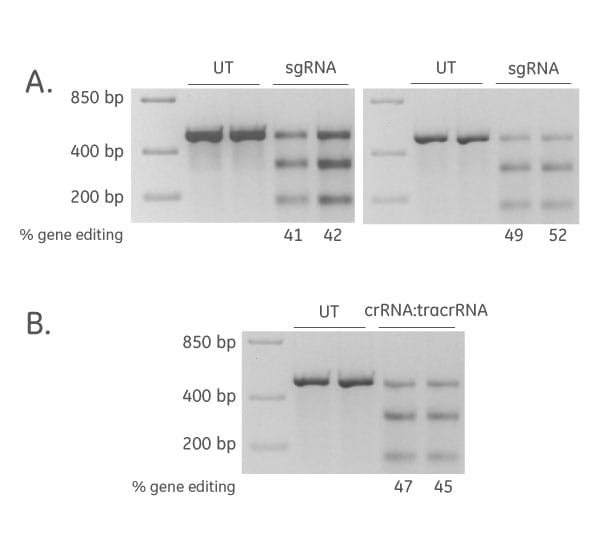
The synthetic sgRNA for target gene editing resulted in high editing efficiency (data shown are from two experiments; (A), and high editing efficiency was also achieved for synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA (B).
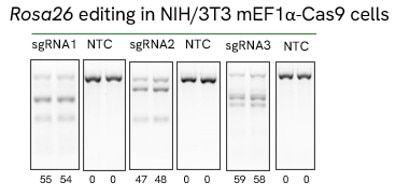
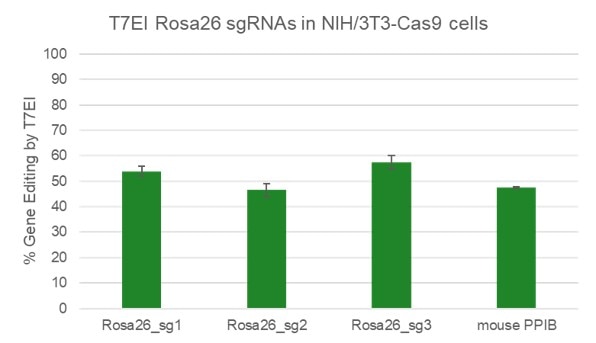
High efficiency of indel generation using Edit-R Rosa26 cutting controls by T7EI
 |
 |
|---|
NIH/3T3 Cas9 stable cells were plated at 10,000 cells/well in a 96 well plate and transfected using 0.2 µL Dharmafect 1 with 25 nM sgRNA (incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes in MEM solution). Cells were harvested at 72 hours post-transfection for direct cell lysis. Primers per spacer region were used to amplify 450-800 bp genomic amplicon from the edited and unedited samples. A hot-start Phusion II touch-down PCR program was used to generate amplicons for each sample. PCR samples were directly incubated with T7 endonuclease I and ran on a 2% agarose SyberSafe gel @ 80V for 90 minutes.
High efficiency of indel generation using Edit-R Rosa26 cutting controls by TIDE
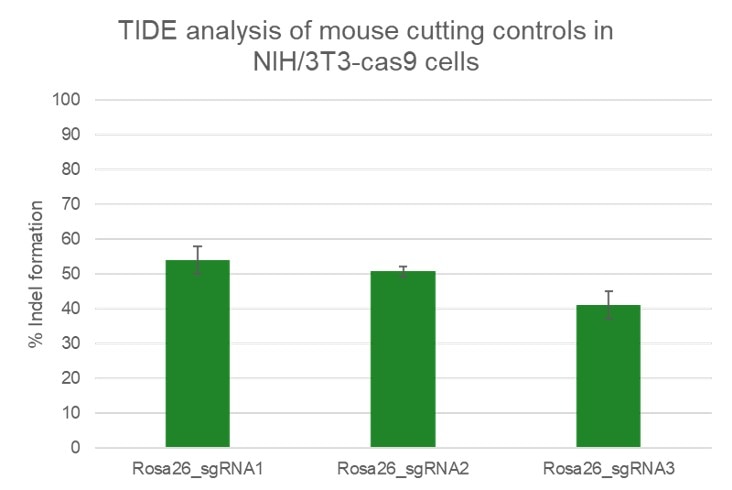
NIH/3T3 Cas9 stable cells were plated at 10,000 cells/well in a 96 well plate and transfected using 0.2 µL Dharmafect 1 with 25 nM sgRNA (incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes in MEM solution). Cells were harvested at 72 hours post-transfection for direct cell lysis. Primers per spacer region were used to amplify 450-800 bp genomic amplicon from the edited and unedited samples. A hot-start Phusion II touch-down PCR program was used to generate amplicons for each sample. PCR samples were sent for Sanger sequencing. Sequencing files were analyzed by tracking of indels by decomposition.
- R. Barrangou, A. Birmingham, et. al. Advances in CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering: lessons learned from RNA interference. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(7) 3407-3419 (2015)
- M.L. Kelley, M.L., Ž. Strezoska, et al. Versatility of chemically synthesized guide RNAs for CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing. J. Biotechnol. 233, 74–83 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.06.011
Application notes
-
A CRISPR-Cas9 gene engineering workflow: generating functional knockouts using Edit-R Cas9 and synthetic crRNA and tracrRNA - Application Note
-
Homology-directed repair with Dharmacon Edit-R CRISPR-Cas9 reagents and single-strand DNA oligos - Application Note
-
Microinjection of zebrafish embryos using Dharmacon Edit-R Cas9 Nuclease mRNA, synthetic crRNA, and tracrRNA for genome engineering - Application Note
-
Optimization of reverse transfection of Edit-R synthetic crRNA and tracrRNA components with DharmaFECT transfection reagent in a Cas9-expressing cell line - Application Note
Posters
-
A Synthetic CRISPR-Cas9 System for Homology-Directed Repair - Poster
-
An algorithm for selecting highly functional and specific guide RNAs for CRISPR-Cas9 gene knockout - Poster
-
Complete alignment identification of CRISPR-Cas9 genomic off-targets using Edit-R CRISPR specificity tool - Poster
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing utilizing chemically synthesized RNA - Poster
-
Homology-directed repair with Edit-R CRISPR-Cas9 and single-strand DNA oligos - Poster
Product data
Protocols
Quick protocols
Safety data sheets
Technical manuals
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering with Cas9 nuclease expression plasmids and Edit-R synthetic RNA - Technical Manual
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering with inducible lentiviral Cas9 nuclease and Edit-R guide RNAs - Technical Manual
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering with lentiviral Cas9 particles and Edit-R synthetic guide RNA - Technical Manual
