Edit-R 化学合成ポジティブcrRNAコントロール
CRISPR-Cas9ゲノム編集の最適なパラメータを確認するための化学合成crRNAコントロール

Please note:crRNAへヌクレアーゼ耐性の安定化化学修飾が追加されたことに伴い、2017年に化学合成crRNAコントロールのカタログ番号が変更されたことに注意してください。これらの変更について詳しくは、featured articleをご覧ください。
Edit-R 化学合成crRNAコントロールは、化学合成sgRNAを用いたCRISPR-Cas9実験において、トランスフェクション条件を最適化し、Cas9ヌクレアーゼ発現を検証するためのポジティブコントロールとして推奨されます。
遺伝子特異的ポジティブコントロールとキットは、ゲノム編集実験を検証するためのDNAミスマッチ検出アッセイ用に設計および検証されています。
-
ヒトおよびマウスのPPIBまたはDNMT3Bを編集する個別Edit-R crRNAコントロール(5 nmolまたは20 nmol):
-
Cyclophilin B (PPIB)
-
DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B)
-
-
以下を含むヒトまたはマウス用のEdit-R crRNAコントロールキット:
-
5 nmolまたは20 nmol Edit-R CRISPR化学合成crRNAコントロール
-
5 nmol Edit-R crRNAコントロール フォワードプライマー
-
5 nmol Edit-R crRNAコントロールリバースプライマー
-
Edit-R Lethal化学合成crRNAコントロールは、ゲノム内の複数のリピート領域を標的にすることにより、用量およびCas9依存的に細胞死を誘導するように設計されたユニバーサルポジティブコントロールです。
Edit-R lethal化学合成crRNA コントロール#1は非常に強力な細胞死を誘導し、lethal コントロール#2は中程度の細胞死を誘導します。これらのコントロールは幅広いダイナミックレンジに対応しており、CRISPR-Cas9ゲノム編集による表現型の高度と中程度の両方の変化を観察することで、CRISPR-Cas9ゲノム編集実験におけるガイドRNA導入を最適化することができます。本コントロールの詳細については、featured articleまたはApplication Noteをお読みください。
注意:コントロールcrRNAにもtracrRNAが必要です。
Edit-R CRISPR-Cas9ゲノム編集
Dharmacon Edit-R CRISPR-Cas9化学合成crRNAプラットフォームは、天然のS. pyogenesシステムに基づいて、哺乳動物細胞でのゲノム編集に3つのコンポーネントを必要とします。
- Cas9ヌクレアーゼ:タンパク質、mRNA、またはCas9ヌクレアーゼをコードする哺乳動物コドン最適化遺伝子配列を発現するレンチウイルスベクター
- 化学的に合成されたtrans-activating CRISPR RNA (tracrRNA)
- 目的の遺伝子標的部位に合わせて設計された化学合成CRISPR RNA (crRNA)
細胞に導入されると、crRNA:tracrRNAとCas9ヌクレアーゼとの複合体が、部位特異的なDNA二本鎖切断(double strand break: DSB:)を生じます。DSBが非相同末端結合(non-homologous end-joining: NHEJ)を介して修復されると、結果として生じる小さな挿入および欠失(indel)がナンセンス突然変異を引き起こし、遺伝子破壊によって機能的なノックアウトが生じます。
crRNAおよびtracrRNA必要量
この表は、推奨されるcrRNA:tracrRNA作業濃度(25 nM:25 nM)を用いて、さまざまなプレート/ウェル形式でリピッドトランスフェクション法を実施できる概算の実験数を示しています。計算では、ピペッティングエラーは考慮されていません。| crRNA nmol | tracrRNA nmol | 96-well plate 100 µL reaction volume | 24-well plate 500 µL reaction volume | 12-well plate 1000 µL reaction volume | 6-well plate 2500 µL reaction volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 | 800 | 160 | 80 | 32 |
| 5 | 5 | 2000 | 400 | 200 | 80 |
| 10 | 10 | 4000 | 800 | 400 | 160 |
| 20 | 20 | 8000 | 1600 | 800 | 320 |
Edit-R lethal crRNAコントロールで処理したCas9発現細胞における細胞生存率の低下
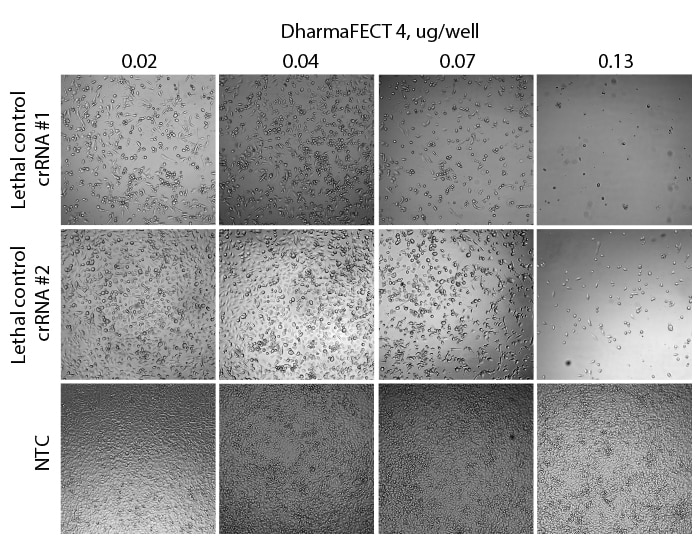
位相差顕微鏡により、NTCと比較して、Edit-R crRNAコントロール#1では強い細胞死表現型が、Edit-R crRNAコントロール#2ではやや中程度の細胞死が明らかに示されました。細胞生存率の低下は、crRNA:tracrRNA複合体の導入に使用したDharmaFECT 4トランスフェクション試薬の量に依存しました。Cas9発現U2OS-プロテアソーム細胞を96ウェルプレートに1ウェルあたり10,000細胞でプレーティングしました。プレーティングから24時間後、0.02-0.13 µg/ウェルのDharmaFECT 4トランスフェクション試薬を用いて、細胞を25 nM crRNA:tracrRNAでトランスフェクトしました。NTC = non-targetingコントロール
lethalコントロールからの細胞死に対する最適トランスフェクション条件は、プロテアソーム依存性表現型と相関する
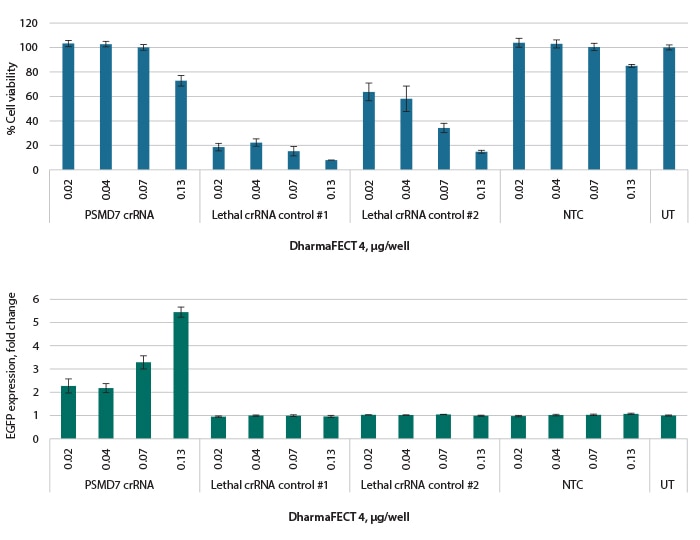
A. 組換えU2OS Ubi[G76V]-EGFP-Cas9細胞を、トランスフェクション試薬量の範囲でレザズリンアッセイを用いて細胞生存率を解析しました。lethalコントロールは用量依存的な細胞死レベルを示します。B. プロテアソーム破壊の読み出しとして、細胞をEGFP発現について解析しました。細胞生存率で示される最適条件では、最適なEGFP発現が再現されました。全ての結果は、トランスフェクションから72時間後のUTに対して正規化しました。UT = 未処理細胞、NTC = non-targetingコントロール
ヒトおよびマウス細胞におけるPPIBの効果的なゲノム編集
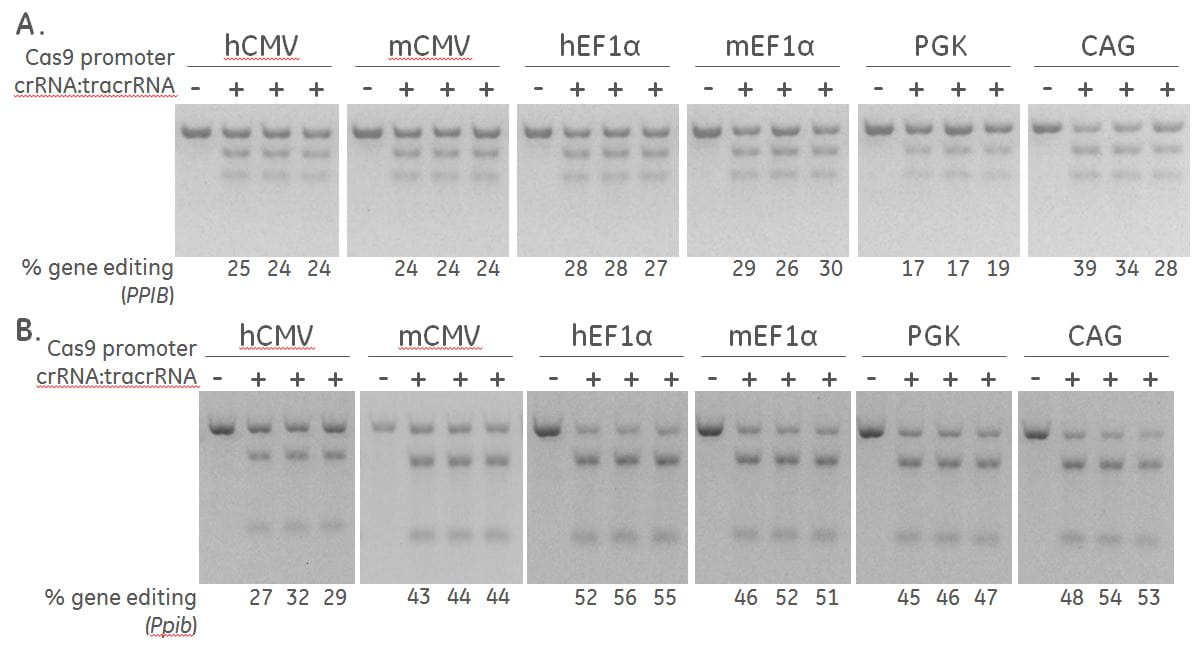
ヒト組換えU2OSユビキチン-EGFPプロテアソーム細胞株(Ubi[G76V]-EGFP)(A)およびマウス線維芽細胞(NIH/3T3)(B)を、Cas9と示されたプロモーターによって駆動されるブラスチジン耐性遺伝子を含むレンチウイルス粒子で安定的に形質導入しました。Cas9-blastRが安定に組み込まれた細胞集団は、トランスフェクションの前に最低10日間、blasticidinで選択しました。DharmaFECT 1およびDharmaFECT 3トランスフェクション試薬をそれぞれ用いて、ヒトPPIB/マウスPpibを標的とする50 nMの合成crRNA:tracrRNAで細胞をトランスフェクトしました。72時間後、ゲノム編集の相対頻度は、トランスフェクト細胞から抽出したゲノムDNAのT7EIを用いたDNAミスマッチ検出アッセイに基づいて算出しました。
非修飾crRNA:tracrRNAまたはヌクレアーゼ耐性修飾crRNAによるPPIBおよびDNMT3Bのゲノム編集の比較
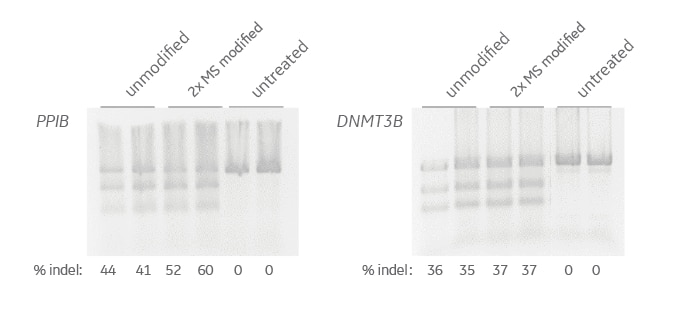
Cas9ヌクレアーゼを発現するHEK293T細胞に、PPIBまたはDNMT3Bを標的とする未修飾のcrRNA:tracrRNA、またはヌクレアーゼ分解に抵抗する修飾(2'-O-メチル;2'OMe)およびcrRNAの5'末端の2つのヌクレオチド上およびtracrRNAの3'末端の2つのヌクレオチド上の骨格ホスホロチオエート結合(PS)を有するcrRNA:tracrRNAをトランスフェクトしました。) T7EI DNAミスマッチアッセイを行い、サンプルを2 %アガロースゲルで分離しました。インデルのパーセンテージを計算し、レーンの下部に示しました。
- R. Barrangou, A. Birmingham,et. al.Advances in CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering: lessons learned from RNA interference.Nucleic Acids Research,43(7) 3407-3419 (2015)
-
M.L. Kelley, Ž. Strezoska, et al. Versatility of chemically synthesized guide RNAs for CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing. J. Biotechnol. 233, 74–83 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.06.011
Application notes
-
Homology-directed repair with Dharmacon Edit-R CRISPR-Cas9 reagents and single-strand DNA oligos - Application Note
-
Optimization of reverse transfection of Edit-R synthetic crRNA and tracrRNA components with DharmaFECT transfection reagent in a Cas9-expressing cell line - Application Note
-
トランスフェクション最適化およびCRISPR-Cas9実験条件の継続的モニタリングのためのEdit-R™ Lethal crRNAコントロール - Application Note
Posters
-
2'-O-methyl phosphorothioate linkage-modified synthetic guide RNAs for efficient CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing and reduced cellular toxicity - Poster
-
A Synthetic CRISPR-Cas9 System for Homology-Directed Repair - Poster
-
An algorithm for selecting highly functional and specific guide RNAs for CRISPR-Cas9 gene knockout - Poster
-
Complete alignment identification of CRISPR-Cas9 genomic off-targets using Edit-R CRISPR specificity tool - Poster
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing utilizing chemically synthesized RNA - Poster
-
Homology-directed repair with Edit-R CRISPR-Cas9 and single-strand DNA oligos - Poster
Product data
Product inserts
Protocols
Quick protocols
Safety data sheets
Technical manuals
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering with Cas9 nuclease expression plasmids and Edit-R synthetic RNA - Technical Manual
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering with inducible lentiviral Cas9 nuclease and Edit-R guide RNAs - Technical Manual
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering with lentiviral Cas9 particles and Edit-R synthetic guide RNA - Technical Manual
Related Products
Cutting control (Safe Harbor) synthetic crRNAs recommended for determination of baseline cellular responses in CRISPR-Cas9 experiments.
精製済みCas9 nuclease mRNAは、化学合成ガイドRNAとのコトランスフェクションで使用することにより完全にDNA-freeのゲノム編集を行えます。
