High-throughput screening with RNAi libraries has provided researchers with an unbiased approach for identifying novel genes involved in biological processes. This method has been used successfully for synthetic lethality screens in cancer cells, identification of host factors exploited by pathogens, and a variety of basic biological screens (for examples, see our listhtt of recommended RNAi Screening References).
Due in part to the potential for off-target effects, one of the most time-consuming steps in the screening workflow is validation of hits identified in the initial screen. A combination of experimental and bioinformatic approaches are typically used to narrow down the list of hits to a manageable number of targets that can be studied in depth. Screeners generally agree that collecting data from multiple independent siRNA sequences, multiple assays, multiple cell lines, and/or complementary techniques are important for generating a list of high-confidence hits. A greater number of data points can help to simplify the stratification of hits.
What are C911 Controls?
One experimental tool for identifying off-targets (false positives) in a siRNA screen is a seed-matched control. These controls are designed to contain the same seed sequence (nt 2-8 of the antisense strand) as the original siRNA in the screen with all or a portion of the remaining sequence altered to prevent target gene knockdown. C911 controls1 are a version of seed-matched controls that are quickly growing in popularity.
C911 Controls
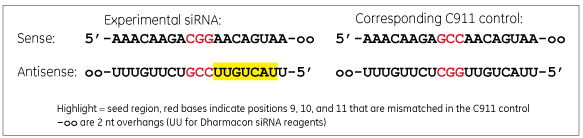
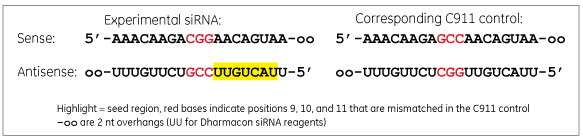
A C911 control has bases in positions 9, 10 and 11 changed to their direct complement compared to the targeting siRNA sequence.
C911 Controls
A C911 control has the same sequence as the experimental siRNA used in the original screen except the bases in positions 9, 10 and 11 are changed to their complement. The mismatches are thought to disrupt cleavage of the intended mRNA target, but still maintain potential off-target effects. Comparison of the original siRNA and the C911 control in a phenotypic assay should distinguish results that are due to down-regulation of the intended target rather than off-target effects.
A C911 control has bases in positions 9, 10 and 11 changed to their direct complement compared to the targeting siRNA sequence.
Experimental Considerations
- We strongly recommend verifying mRNA expression levels by qPCR for both targeting and C911 siRNAs before drawing conclusions about false positives. This will ensure the phenotype correlates with knockdown of the intended target.
- A C911 control could have a perfect match to another gene target, thereby having its own on-target knockdown. The sequences should be assessed for 19/19 matches to other transcripts.
Designing C911 controls
The C911 Calculator
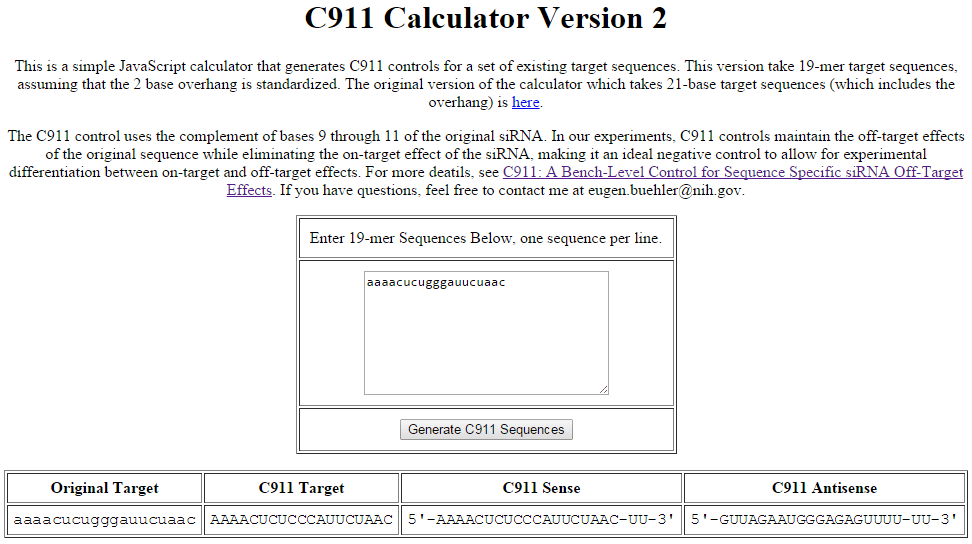
The C911 design is simple to generate manually for a small number of siRNAs. For screeners working with a larger list of siRNAs, the authors of the C911 publication have developed a tool designed to quickly convert your original siRNA target sequences into C911 control target sequences. To design C911 controls for Dharmacon siRNAs using this tool, please follow these steps:
- Locate the siRNA target sequences provided in the plate map file for your siRNA library or on the Product Transfer Form for siRNAs ordered in tubes.
- Paste or enter the siRNA target sequence(s) into the C911 Calculator. Multiple input sequences can be entered on separate lines.
- Click the "Generate C911 Sequences" button.
- The results in the "C911 Target" column are the sequences that should be entered in our custom siRNA synthesis interface to make the C911 control (see "Ordering C911 controls").
c911 Calculator
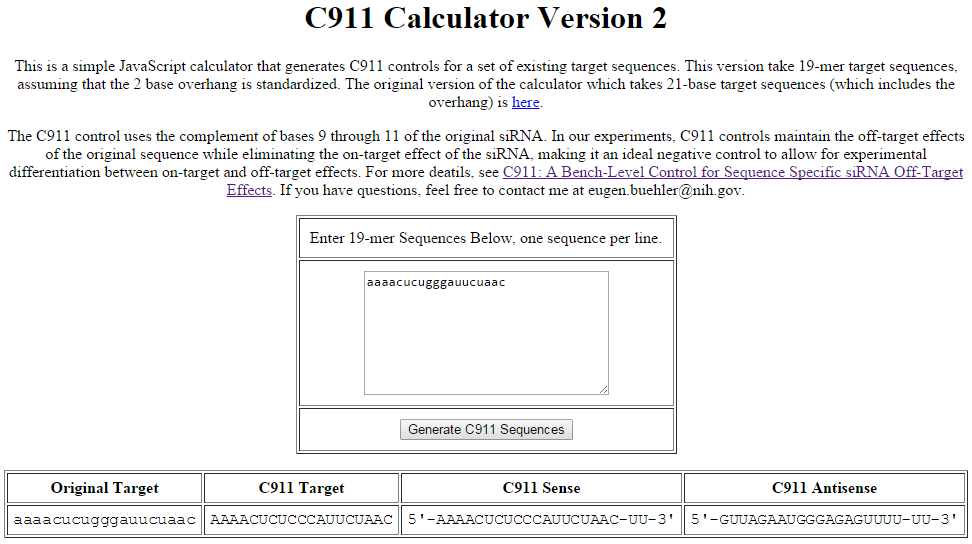
Example of C911 control sequence generation using the C911 Calculator available from the NIH. The sequence in the column labeled "C911 Target" is the input for custom synthesis to generate a C911 control based on the input experimental siRNA sequence.
c911 Calculator
Ordering C911 controls
C911 controls must be ordered as custom siRNAs. These orders can be placed using our online custom siRNA ordering tool.
- Indicate an oligo name and desired size. Default processing and overhangs on these ordering pages match our catalog siRNA and are recommended for these controls.
- Select siRNA Type. It is strongly recommended to use the same modification as the original siRNA to which the C911 will be compared. For example, if the targeting siRNA has the ON-TARGETplus modification, select ON-TARGETplus synthesis for the C911 control. Please note that a percentage of siGENOME siRNAs have the ON-TARGET modification. For help identifying which of your siGENOME siRNAs have this modification, you may send a list of catalog numbers to Scientific Support.
- Enter or paste the "C911 Target" sequence(s) from the C911 Calculator into the Target Sequence(s) field of the custom synthesis order page. If you wish to have a logical name associated with each siRNA when using the multiple siRNA order form (recommended), sequences and names must be copied from a spreadsheet and pasted into the tool. Sequences should be in the left column and names should be in the right column. Copy both columns together and paste into the Target Sequences box.
Alternatively, a list of C911 sequences may be provided directly to Scientific Support. Please provide desired siRNA names, processing, overhangs, and synthesis scale.
References
- Buehler, E. et al. C911: A Bench-Level Control for Sequence Specific siRNA Off-Target Effects. PLOS One 7, Dec 14 2012
Order Products
Custom siRNA Synthesis
siRNA customization has never been easier
Custom siRNA
Easy online ordering of standard, Dharmacon enhanced, and modified siRNAs
rnai-screening-libraries
Ensure screening success when you choose from our siRNA, shRNA and microRNA libraries.
RNA Interference Products
Dharmacon RNAi products encompass the most complete portfolio of innovative tools for transient, long-term, inducible and in vivo RNAi applications.
Helpful Resources
Seed sibling controls for RNAi hit validation
Uncover potential seed-based off-targets from siRNA screens
siRNA Screening: Development of Hit Stratification Strategies - Poster
We compared 2 strategies for identification of high confidence hits in RNAi screens
Off-Target Effects - Tech Note
Bioinformatics, novel chemical modifications, and siRNA pooling significantly decrease off-target effects
Recommended Reading: RNAi Screening References
Selected publications of general interest to researchers performing RNAi (siRNA, shRNA, microRNA) libraries for functional genomic screening.
