TNF Alpha Signaling Cell Lines
TNF alpha signalling is an essential part of the immune system as inhibits tumorigenesis, prevents viral replication and is an endogenous pyrogen inducing fever and apoptosis. Dysregulation of this pathway has been implicated in a variety of disorders including cancer, autoimmune diseases, Alzheimer’s disease and depression.
Various anti-TNF drugs have been approved for the treatment of inflammatory related diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease and psoriasis.
TNF Alpha overview
TNF alpha exists as a transmembrane protein arranged in stable homotrimers. A soluble form of TNF alpha can be produced by proteolytic cleavage of the membrane bound form. Both forms are biologically active although the specific function of each is controversial.
TNF alpha is recognized by two main receptors: TNFR1 (TNF Receptor 1, CD120a) and TNFR2 (TNF Receptor 2, CD120b.
TNFR1
TNFR1 is expressed by most tissues and can be activated by both forms of TNF alpha.
TNFR2
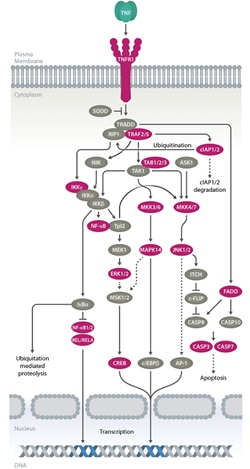
TNFR2 is mainly expressed in the immune system and responds to the membrane bound form of TNF alpha. Binding of TNF alpha to TNFR1 results in conformation changes in the receptor and recruitment of TRADD, this in turn binds FADD, TRAF2 and RIP and results in activation of downstream pathways such as, NF-κB, JNK and p38 MAPK pathways and death signaling. The NF-κB and MAPK pathways induce complex and long lasting transcriptional modifications and the production of interleukins and chemokines
Explore our popular knockout cell lines for TNF Alpha Signaling
Order products
Human knockout HAP-1 cells
The single largest bank of isogenic cell lines with over 7,500 cell lines to choose from and trusted by academia, biotech, and pharma research labs.
Cancer-related cell lines
Choose from over 300 knock-in and knockout cell line models in many standard cancer cell lines such as DLD1, MCF10A, and HCT116.
Cas9 Stable Cell Lines
Simplify gene editing experiments with stably expressing Cas9 cell lines
CRISPRmod CRISPRa dCas9-VPR Stable Cell Lines
Streamline CRISPR activation experiments with stably expressing dCas9-VPR cell lines
