The CRISPRa system
The Dharmacon™ CRISPRmod CRISPRa system requires two components: a specialized dCas9 fused to activator proteins (VPR), and a guide RNA specifically designed to target the region immediately upstream of a gene’s transcriptional start site (TSS). The guide associates with dCas9-VPR and directs the activator complex to the DNA target site (figure 1). Horizon offers lentiviral and transient approaches for both activator protein and guide introduction.

Figure 1. Diagram of dCas9-VPR with sgRNA targeting a gene’s promoter region.
dCas9-VPR
In CRISPR-Cas9 based CRISPRa systems, the native Cas9 DNA-cutting functionality has been obliterated by point mutations in the RuvCI and HNH nuclease domains. These mutations change the protein to a deactivated, or dead, Cas9 (dCas9). This dCas9 protein is further engineered by fusing various transcriptional activators.
Horizon's CRISPRa system relies on the popular dCas9-VPR activation system. Other transcriptional activation strategies, such as SAM, are also described here. The dCas9-VPR system works because of the fusion of the dCas9 to three transcriptional activators (VP64, p65, and Rta)1-7 at the C-terminal end.
CRISPRa guide RNA
CRISPRa guide RNAs target sequences upstream of the target gene's promoter region or the transcriptional start site (TSS) to result in activation3,5. Designing functional guide RNAs can be challenging, as TSSs are not always well annotated or are inaccessible due to other protein factors. Horizon's CRISPRa guide RNA designs use a published CRISPRa v2 algorithm developed via machine learning techniques8. The algorithm used FANTOM and Ensembl databases to predict the TSSs and incorporate chromatin, position, and sequence data to predict highly effective guide RNA designs. Additional challenges arise when genes have alternative TSSs (6.8% of genes), and a small number of genes (0.1%) have more than two TSSs. Horizon lists ten guide RNA designs per TSS, ranked in order of predicted functionality.
Horizon's CRISPRa guides are available as either synthetic sgRNA or crRNA or expressed sgRNA formats.
Pooling increases CRISPRa efficiency
Pooling multiple CRISPRa guide RNA designs has been found to produce either increased gene activation (Figure 2a) or gene activation that is equivalent to the most functional individual crRNA (Figure 2b).
We examined the overlap between the published algorithm designed guide RNAs and found that for most genes (> 70%), there is little to no overlap of the guide RNA target sites. For these genes, we typically see an increase in the level of activation when pooling the gRNAs. Only a small subset of genes (~12%) overlap all four designs at the TSS. For these genes, we have found that the pool typically works similarly to the most effective gRNA. Overall, pooling is an excellent strategy to drive maximal gene activation. Pooling is also beneficial to decrease an experiment's scale, for example, when performing an analysis of multiple genes in an arrayed plate format.
Pooling guide RNAs enhances transcriptional activation
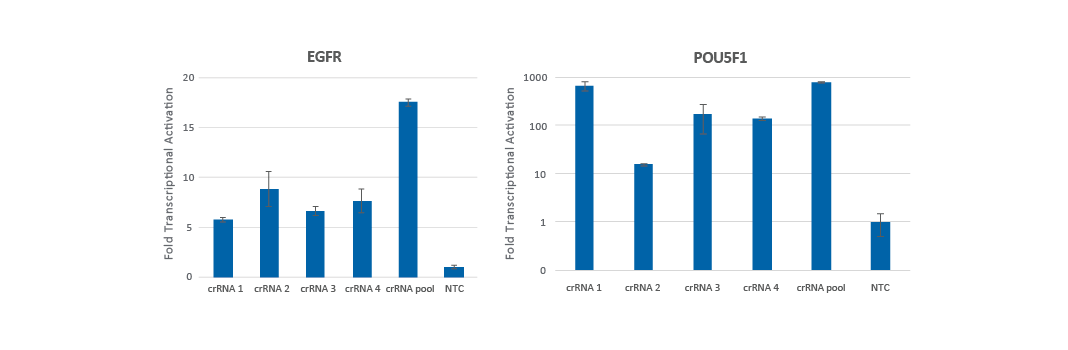
Figure 2. U2OS cells stably expressing integrated dCas9-VPR were plated at 10,000 cells/well and transfected using DharmaFECT 4 Transfection Reagent with CRISPRa synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA (25 nM) targeting EGFR (A) or POU5F1 (B). The pre-designed crRNAs were used either individually or pooled (to a total concentration of 25 nM). Cells were harvested 72 hours post-transfection, and the relative gene expression was calculated using RT-qPCR. Each gene's relative expression was calculated with the ∆∆Cq method using GAPDH as the housekeeping gene and normalized to a non-targeting control.
sgRNA is as effective as crRNA:tracr for CRISPR activation
Robust CRISPRa activation can be achieved in multiple formats. Figure 4 shows that crRNA:tracrRNAs work similarly to sgRNA pools for activation of multiple gene targets.
CRISPR activation in stable dCas9-VPR-expressing mouse cells and transfected individual and pooled single sgRNA reagents

Figure 3. NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing integrated CRISPRa dCas9-VPR (driven by mCMV promoter) were plated at 10,000 cells/well and transfected using DharmaFECT 1 Transfection Reagent (0.2 uL/well) with CRISPRa synthetic single guide RNA (sgRNA) targeting ttn or pou5f1 genes. CRISPRa sgRNAs were used either individually or pooled (to an individual or pooled concentration of 25 nM). Gene expression was assessed using RT-qPCR as described in Figure 2.
Confirming gene activation
There are many methods to confirm gene activation, including RT-qPCR, Western blots, or immunofluorescence analysis. Typically, the fastest and easiest way to measure the relative change in target gene expression levels between samples treated with a non-targeting control and CRISPRa guide RNAs is RT-qPCR. RT-qPCR analysis works with either the SYBR green method or probe-based gene expression assays. One thing to note when performing RT-qPCR for gene activation is the gene expression level may be undetectable before CRISPRa. In this case, when using the ∆∆Cq method of analysis, an arbitrary value representing the qPCR instrument's detection limit is used as a place holder for "non-detectable" as a non-zero value is necessary to perform the calculation. In most cases, this value will be between 35 and 40, depending on the number of programmed cycles and the instrument Cq determination method. Many protocols recommend adding additional cycles (up to 45 total) to standard qPCR cycling conditions. An important consideration when designing CRISPRa experiments is that the level of gene activation correlates with the basal target expression level of each respective cell type. Higher activation (100-10,000-fold) may be observed for low basal expression genes, whereas genes that are moderate to highly expressed have lower fold activation (generally less than 100-fold). Before setting out to perform CRISPRa, it is worthwhile to determine your cell line of interest's basal expression level to set expectations on the activation you can achieve. For example, the gene POU5F1 encodes for a transcription factor (OCT4) highly expressed in pluripotent cells like iPSCs but is typically low expressed when cells are differentiated. POU5F1 is one of the genes that we recommend as a positive control, but this would not be a logical choice when working with stem cells. Robust relative gene activation of POU5F1 in iPSCs can be achieved and a U2OS-dCas9-VPR integrated cell population (a bone osteosarcoma cell line) (Figure 4). As anticipated, we see low transcriptional activation of POU5F1 in the iPSCs (~1.2 fold) but high transcriptional activation in the bone osteosarcoma cells (~600 fold).
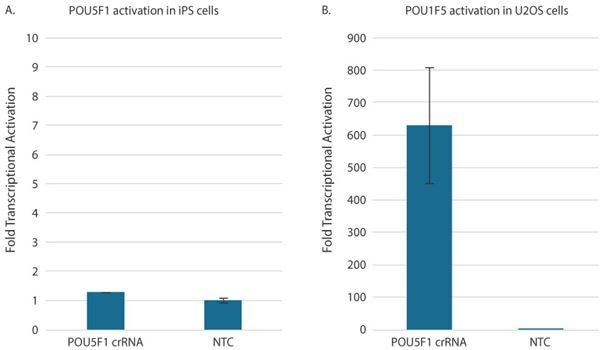
Figure 4: Relative gene activation of POU5F1 in iPSCs (A) and a U2OS-dCas9-VPR integrated cell population (a bone osteosarcoma cell line) (B).
Experimental Considerations for CRISPRa
There are many options and considerations for CRISPRa experimental conditions. Generally, users achieve the most robust gene activation when working with a stable population of dCas9-VPR cells. For extended time point assays (more than 96 hours), many choose lentiviral sgRNA. For short-term assays (less than 96 hours), synthetic sgRNA or crRNA:tracrRNA or plasmid sgRNA give equivalent gene activation.
| dCas9-VPR source | Guide RNA format | Delivery method | Recommendations for use & benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CRISPRa dCas9-VPR stable cells or CRISPRa dCas9-VPR lentiviral particle transduction |
CRISPRa synthetic sgRNA | Transfection or electroporation |
|
| CRISPRa synthetic crRNA + tracrRNA | |||
| CRISPRa lentiviral sgRNA particles | Transduction |
|
|
| CRISPRa dCas9-VPR mRNA | CRISPRa synthetic sgRNA | Co-transfection or electroporation |
|
| CRISPRa synthetic crRNA + tracrRNA | |||
| CRISPRa dCas9-VPR lentiviral plasmid | CRISPRa lentiviral sgRNA plasmid | Co-transfection or electroporation with dCas9-VPR plasmid |
|
| CRISPRa all-in-one dCas9-VPR + sgRNA | Transduction |
|
|
CRISPRa product platform
We offer several options to use CRISPRa for transcriptional activation.
CRISPRa dCas9-VPR:
- Start with premade stable cell lines expressing dCas9-VPR.
- Make stable cells using purified plasmid or lentiviral particles in an expression vector with your choice of a promoter.
- Use entirely DNA-free dCas9-VPR mRNA (with options of EGFP or puromycin markers for enrichment).
CRISPRa guide RNA:
We offer pre-designed CRISPRa synthetic crRNA, synthetic sgRNA, lentiviral sgRNA or All-in-one Lentiviral sgRNA for all human and mouse genes.
CRISPRa synthetic crRNAs are supplied as individual reagents, a set-of-4, or a pool (an equimolar mix of the top four designs). Guides come in tubes or multi-well plates using the Cherry-pick Library Plater. This guide format must be used with synthetic tracrRNA.
CRISPRa synthetic sgRNAs are supplied as individual reagents, a set-of-3, or a pool (an equimolar mix of the top three designs). Guides come in tubes or multi-well plates using the Cherry-pick Library Plater.
CRISPRa lentiviral sgRNA and All-in-one Lentiviral sgRNA are supplied as individual reagents or a set-of-4, in either purified lentiviral particles or glycerol stocks.
When applicable, an additional four guide RNAs for alternative TSS are labeled as P1 and P2 (alternate promoter). If the CRISPRa guide RNA options for your gene have both P1 and P2 designations, it may be beneficial to test both for your experiment. If the CRISPRa guide RNAs for your gene do not have a P1 or P2 label, only a single start site is defined. For the small number of genes with more than two TSS identified, we only offer P1 and P2 as catalog items but can manufacture any guide RNAs based on designs from the published algorithm8 as a custom request.
References
- L. A. Gilbert et al., CRISPR-Mediated Modular RNA-Guided Regulation of Transcription in Eukaryotes. Cell. 154, 442–451 (2013).
- W. Cheng et al., Multiplexed activation of endogenous genes by CRISPR-on, an RNA-guided transcriptional activator system. Cell Res. 23, 1163–1171 (2013).
- L. A. Gilbert et al., Genome-Scale CRISPR-Mediated Control of Gene Repression and Activation. Cell. 159, 647–661 (2014).
- M. E. Tanenbaum, L. A. Gilbert, L. S. Qi, J. S. Weissman, R. D. Vale, A protein-tagging system for signal amplification in gene expression and fluorescence imaging. Cell. 159, 635–646 (2014).
- S. Konermann et al., Genome-scale transcriptional activation by an engineered CRISPR-Cas9 complex. Nature. 517, 583–588 (2015).
- Chavez et al., Highly efficient Cas9-mediated transcriptional programming. Nat. Methods. 12, 326–328 (2015).
- J. G. Zalatan et al., Engineering complex synthetic transcriptional programs with CRISPR RNA scaffolds. Cell. 160, 339–350 (2015).
- M. A. Horlbeck et al., Compact and highly active next-generation libraries for CRISPR-mediated gene repression and activation. eLife. 5, e19760 (2016).
- Chavez et al., Comparison of Cas9 activators in multiple species. Nat Methods. 7, 563–567 (2016)
Order products
CRISPR guide RNA
Synthetic and lentiviral expressed CRISPRa crRNAs for highly specific transcriptional overexpression of any human gene.
'CRISPRa-ready' dCas9-VPR expressing stable cell lines
Choose from a range of common cell line backgrounds, then deliver your CRISPRa guide RNA for direct gene activation.
CRISPRmod Controls
Positive and non-targeting controls to ensure your CRISPRi or CRISPRa experimental conditions
dCas9-VPR reagents
Purified dCas9-VPR mRNA or lentiviral particles offer solutions for any CRISPRa workflow
