- Non-mammalian research tools
- Yeast Cross and Capture System Collection
Yeast Cross and Capture System Collection

Created by researchers in the Stagljar Lab at the University of Toronto, the Yeast Cross and Capture System, a novel “bait” MATa strain assay, is used for assessment of protein–protein interactions. This assay employs a pulldown of differently tagged yeast strain arrays when a specific gene tagged with 6xHIS is mated with a “prey” MATalpha with a specific gene tagged with VSV to generate a diploid organism. The tagged protein and any interacting molecules can then be pulled down via the 6xHIS tag and the VSV can be detected on a western blot with an anti-VSV antibody.
Features
Following diploid growth and cell lysis, extracts are incubated with nickel beads, allowing isolation of the 6xHIS-tagged bait and its associated proteins. Bound proteins are examined by immunoblot analysis for the presence of the bait and prey proteins using anti-V5 and anti-VSV antibodies. If the prey protein binds to the nickel beads in a bait-dependent manner, a PPI is inferred. Conversely, the absence of the prey protein in a pulldown reaction suggests that the two proteins fail to interact.
Highlights
- 6xHIS tag on bait Mat-a strain allows for pull-down of interacting protein complexes
- Anti-V5 antivody can be used to detect both bait and prey proteins
- Anti-VSV antibody can be used to specifically detect prey protein
- Amenable to high-throughput screens
Strain Information
- Baits are in the BY4741 (MATa ura3Δ0 leu2Δ0 his3Δ1 met15Δ0) background strain.
- Preys are in BY4742 (MATα ura3Δ0 leu2Δ0 his3Δ1 lys2Δ0) background strains.
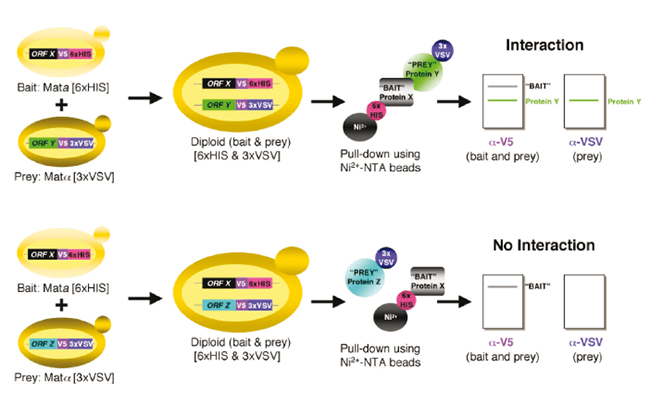
A strain containing the bait ORFX tagged with a V5 epitope and six histidines (6xHIS) is crossed with strains that contain prey ORFY or ORFZ tagged with a V5 epitope followed by a triple VSV tag (3xVSV). Diploids, which express both tagged bait and prey, are grown on selective medium. Protein extracts from the diploids are then incubated with nickel beads (Ni2+ -NTA), allowing isolation of bait (Protein X–6xHIS) and bait-associated prey protein (Protein Y–3xVSV), whereas a non-interacting protein (Protein Z–3xVSV) will not bind. Proteins are then separated by SDS-PAGE, and blots are probed for bait and prey (anti-V5 antibody) and specifically for the prey (anti-VSV antibody) by immunoblot (Suter et al., 2007).
Note
We provide certain clone resources developed by leading academic laboratories. Many of these resources address the needs of specialized research communities not served by other commercial entities. In order to provide these as a public resource, we depend on the contributing academic laboratories for quality control.
Therefore, these are distributed in the format provided by the contributing institution "as is" with no additional product validation or guarantee. We are not responsible for any errors or performance issues. Additional information can be found in the product manual as well as in associated published articles (if available). Alternatively, the source academic institution can be contacted directly for troubleshooting.
Individual Clones
Within 2 to 3 business days of receiving your order, we will ship your clone at room temperature via express delivery. Store the stock clone at –80°C. Clones are provided as a live culture in a 2 mL tube. Each tube contains YPD + G418 (200 μg/mL) + 15% glycerol.
Bulk Orders
Orders of greater than 50 clones will be provided in microtiter plates. These will ship on dry ice via overnight delivery and should be stored at –80°C immediately upon receipt.
Complete Collection
Orders for the entire collection are provided in 96-well microtiter plates. These will ship on dry ice via overnight delivery and should be stored at –80°C immediately upon receipt.
- B. Suter et al., Examining protein–protein interactions using endogenously tagged yeast arrays: The Cross-and-Capture system. Genome Res. 17(12), 1774-1782 (December 2007).
