- Dharmacon Screening libraries
- Edit-R Human All-in-one Lentiviral sgRNA Whole Genome Pooled Library
Easily knockout thousands of genes at the DNA level with a single transduction of Edit-R All-in-one sgRNA pooled lentiviral pooled library eliminating the need to perform sequential transductions.
This library format is beneficial for performing knockouts in difficult-to-transfect or primary cells allowing for efficient genomic screening facilitating advancements in genetic research and therapeutic discovery.
The choice of promoters (mCMV and hEF1α) allows for optimal Cas9 nuclease expression in the cells of interest.
The ability of CRISPR guide RNA to create a double-strand break in target DNA causing functional protein disruption can vary based on the guide RNA (gRNA) sequence and position in the targeted gene. To address this, the Dharmacon Edit-R algorithm provides highly specific and functional RNA guides across the human genome.
| Schematic map of the Edit-R All-in-one lentiviral sgRNA vector |
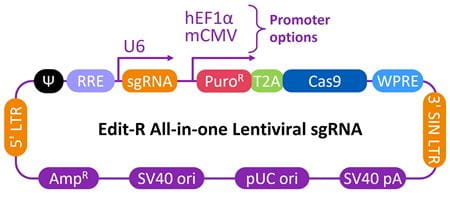 |
The Edit-R CRISPR RNA algorithm generates guide RNA sequences with:
- An optimized alignment program with rapid and thorough specificity analysis, including detection of multiple mismatches and gapped alignments
- Increased functional knockout of targeted genes through systematic assessment of over 1100 guide RNAs to identify characteristics critical for functional gene disruption, not just generation of indels
- New! Edit-R human sgRNA designs have been updated to the latest RefSeq in 2025 providing the most specific and genomically relevant guides for producing efficient protein knockout. This allows the Edit-R algorithm to target the latest genome annotations more accurately and efficiently providing you with the best solution for your research needs. Please reach out to Scientific Support if you have any questions.
Using the Edit-R CRISPR RNA algorithm, we have designed lentiviral sgRNAs showing highly efficient gene knockout at single-copy integration levels required for pooled lentiviral screens.
Highlights:
- Efficient All-in-one vector system utilizing single lentiviral vector for both Cas9 and gene-specific sgRNA expression
- Rationally designed Edit-R lentiviral sgRNAs mediate efficient gene knockout with unparalleled specificity using a functionally validated proprietary algorithm
- Deep and broad coverage with 4 or 8 sgRNAs per gene across the human genomes for increased hit confidence
- Multiple promoter options for robust editing in biologically relevant cell types
- High quality, concentrated, purified lentiviral particles for direct transduction with minimal cytotoxicity; delivered at titers of ≥ 2 x 107 TU/mL
Each Edit-R All-in-one lentiviral sgRNA pooled screening library includes:
- ≥ 2 x 107 TU/mL (± 20%) lentiviral particles in 10 x 100 µL aliquots with mCMV or hEF1α promoter options
- Four or eight sgRNAs per gene targeting coding genes in the NCBI Reference Sequence Database
- 100 non-targeting sgRNA negative controls bioinformatically confirmed to not align with (target) any gene in the human genome
- A data file containing complete library information, including: gene annotations, sgRNA target sequences, complete list of controls, and counts per millions of mapped reads
Products recommended in our validated protocol:
- Vector-matched Edit-R EGFP delivery controls for transduction optimization and promoter selection
- NEW: NGS Library Prep Kit (Recommended)
- Primer set options available for hEF1α and mCMV promoters and at two different sizes for 12 or 24 whole genome screens
- Designed to amplify and sequence sgRNA constructs from gDNA without bias
- One complete solution for sequencing on an Illumina® platform without the need for additional reagents
Information on Edit-R Lentiviral sgRNA pooled library coverage
The number of genes and constructs are subject to change at any time without notice. Clone and gene counts are available upon request. Contact Scientific Support
Volume of lentiviral particles required for whole genome screening
| Fold representation | Replicates | sgRNAs per gene | Volume of lentiviral particles |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 2 | 4 | 1.6 mL |
| 200 | 2 | 8 | 3.1 mL |
| 400 | 2 | 4 | 3.1 mL |
| 400 | 2 | 8 | 6.1 mL |
| NGS Library Prep Kit Contents | Small: 12 Whole Genome Screens | Large: 24 Whole Genome Screens |
|---|---|---|
| NEXTFLEX® PCR Master Mix (green cap) | 3600 μL | 7200 μL |
| Dharmacon HIT Identification Primers (orange cap) | 300 μL | 600 μL |
| NEXTFLEX® PCR II Barcoded Primer Mix | 4 μL | 4 μL |
| Resuspension Buffer | 12 mL | 24 mL |
| Nuclease-free water | 8 mL | 16 mL |
| Cleanup Beads | 7 mL | 15 mL |
Gene knockout screening workflow using the Edit-R All-in-one Lentiviral Pooled Library platform
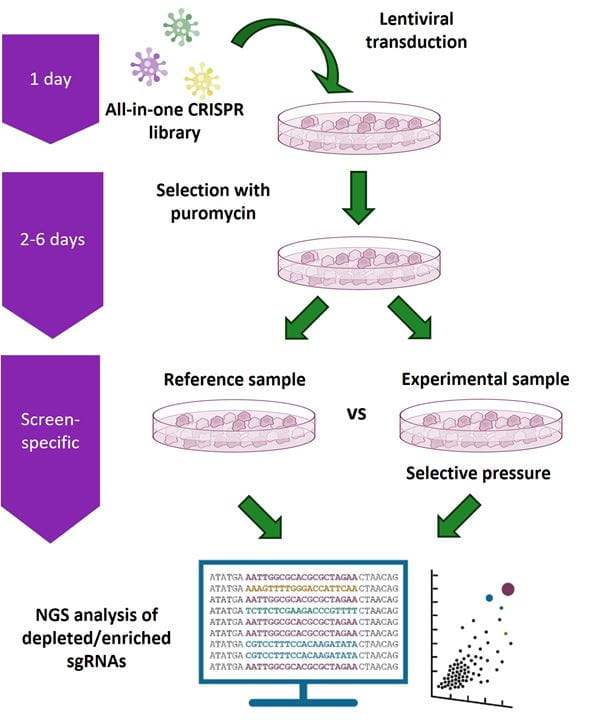
Cells are transduced at a low multiplicity of infection (MOI) with an Edit-R All-in-one Lentiviral Pooled Library and selected with puromycin. Transduced cells are split into reference and experimental populations for application of a selective pressure and/or phenotypic selection. Genomic DNA is then isolated from the reference and experimental populations of transduced cells and sgRNA constructs within the isolated gDNA are amplified using vector-specific NGS Library Prep Kits. Samples can then be multiplexed and sequenced on an Illumina® platform. Custom sequencing read primers are not required. The integrated sgRNA sequences in both reference and experimental samples are identified and relative abundance compared. sgRNA constructs that are enriched or depleted are identified as hits to be confirmed and studied further using individual Edit-R All-in-one Lentiviral sgRNAs in additional phenotypic and/or biochemical assays.
High quality pooled screening begins with rigorous lentiviral pooled library production
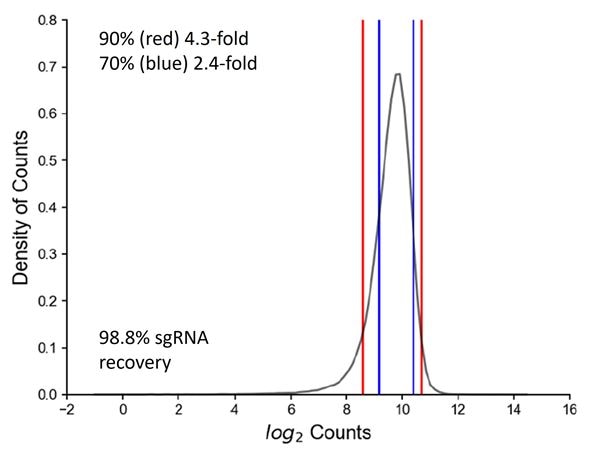
High quality pooled screening begins with rigorous lentiviral pooled library production. An Edit-R Human All-in-one Lentiviral Whole Genome Pooled Library comprising 4 lentiviral sgRNAs per gene was produced and the quality of the plasmid DNA library was verified by next-generation sequencing (NGS). Counts per million mapped reads were obtained to determine the percent-recovery of input sgRNAs (99.8%) and that the distribution of 90% and 70% of the sgRNAs in the pool are within 6.5- and 3.2- fold of each other, respectively, indicating near perfect sgRNA recovery and uniform distribution of sgRNAs.
Matched fluorescent delivery controls enable rapid functional titering and selection of optimal promoter prior to screening

Matched fluorescent delivery controls enable rapid functional titering and selection of optimal promoter prior to screening. DU145 (A) and Jurkat (B) cells were transduced with 5-fold dilution series of Edit-R GFP Delivery controls mCMV (green) and hEF1α (purple) with functional titering units (TU) derived in HEK293 cells. At 72 hours post-transduction, the percentages of EGFP-expressing cells were quantified by flow cytometry. Dilutions exhibiting between 5 to 25% EGFP-expressing cells can be used to calculate the relative functional titer in the cell line of interest and the relative transduction efficiency of the cell line. The percentages of EGFP-expressing cells or mean fluorescence intensity of EGFP-expressing cells at a given dilution (exhibiting 5-25% EGFP-expressing cells) can be used to compare promoter activity in the cell line. While both promoters are similarly active in Jurkat cells, the mCMV promoter is substantially more active than the hEF1α promoter in DU145 cells.
Edit-R functionality scores correlate to editing efficiency
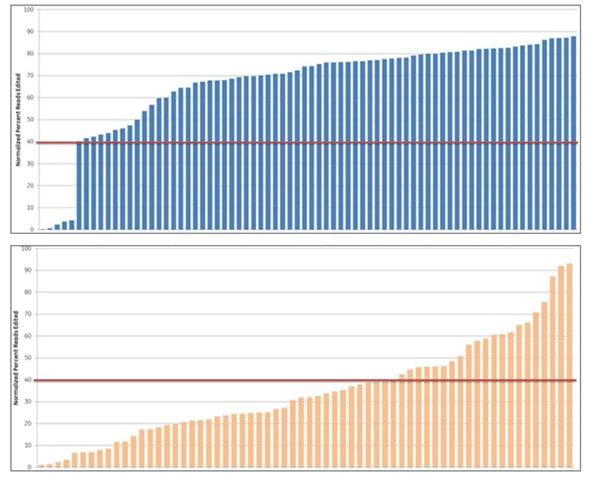
Algorithm scores correlate with editing efficiency (NGS analysis of indel formation). Ten crRNAs with highest algorithm score (blue) and ten crRNAs with lowest algorithm score (orange) targeting 10 genes were transfected in HEK293T cells that stably express Cas9 and assessed for editing by Next Generation Sequencing. The Cas9-HEK293T cell line was transfected with 50 nM crRNA:tracrRNA. Seventy-two hours post-transfection, cells were lysed and Nextera transposon-adapted amplicons spanning each crRNA site were generated for every treated sample as well as for a matched control amplicon from untransfected samples. Samples were indexed using the Nextera 96-well index kit and pooled for sequencing on a MiSeq instrument (paired end reads, 2 x 300 length). Reads that passed NGS quality filtering criteria were aligned to the reference file (Bowtie2 v2.1.0). Percent perfect reads were calculated and normalized to the control untransfected samples (Samtools v0.1.12a); the data is presented as normalized percent edited.
High Edit-R functionality scores correlate with increased functional gene knockout
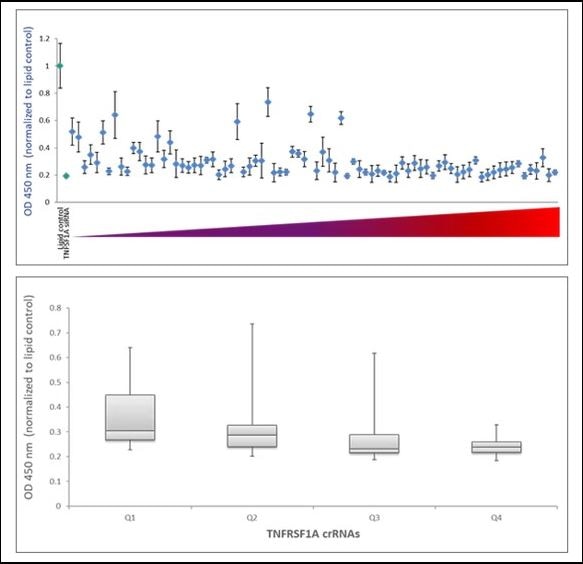
Examination of functionality of TNFRSF1A crRNAs by ELISA assay for soluble TNFRSF1A
To examine the ability of the algorithm-designed gRNAs to predict efficient functional gene knockout at the protein level, tested for correlation of the algorithm scores with effects on target-gene protein level or activity in specific functional assays. We first examined the functionality of 79 gRNAs targeting TNFRSF1A (encoding the soluble portion of TNFRSF1A protein) for their ability to cause a decrease of the TNFRSF1A protein level, as measured by an TNFRSF1A ELISA assay. Figure 5A shows the effect of all crRNAs, arranged by algorithm-predicted functionality scores, on the TNFRSF1A protein level in the cell medium. The crRNAs with high algorithm scores show high functional gene disruption, measured as a decrease at the target gene protein levels. Among the crRNAs with low scores, there is higher variability of the functionality with many guides showing low ability for functional gene knockout (Figure 5A). This is clearly depicted by a box-plot representation of the functionality of crRNAs that is divided in 4 quartiles based on algorithm score, from low to high. The medians, distribution of data between the lower and upper quartile and the minimum and maximum values demonstrate that algorithm designed high-scoring crRNAs demonstrate increase functionality in a protein knockout assay (Figure 5B).
A. U2OS-Proteasome cells with integrated Cas9 (under CAG promoter) were plated in 96-well plates at 10,000 cells per well. 24h after plating, cells were transfected with 50 nM crRNA:tracrRNA using 0.2 µg/well of DF4. siRNA targeting TNFRSF1A was used as a positive control and data was normalized to the negative control (lipid only). Cell medium was collected 72 h after transfection and assayed for soluble TNFRSF1A using Quantikine Human sTNF RI/TNFRSF1A Quantikine ELISA Kit (R&D Systems).
B. Box plot representation of the functionality of the TNFRSF1A crRNAs in the ELISA assay for soluble TNFRSF1A –crRNAs are divided in 4 quartiles based on their algorithm score from low to high (Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4).
Whole-genome screen using Edit-R Human All-in-one Lentiviral Pooled Library identifies high-confidence resistance hits in A375 cells treated with Vemurafenib
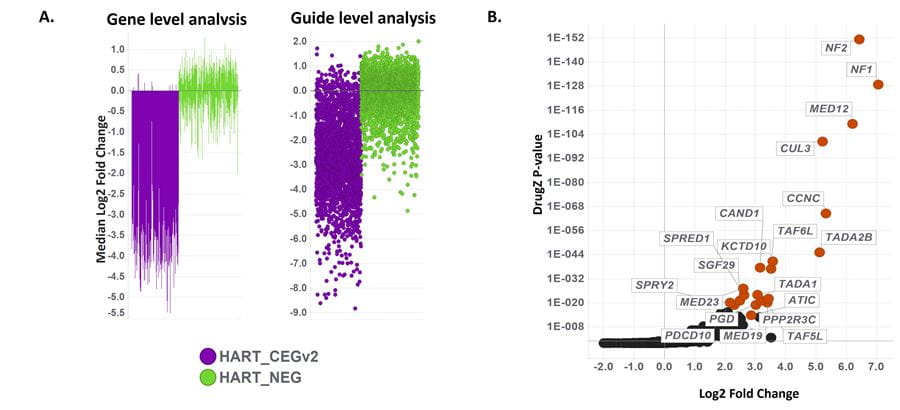
High confidence resistance hits and distinct essential gene dropout with the Edit-R Human All-in-one Lentiviral Pooled Library in A375 melanoma cells treated with vemurafenib (PLX-4032) for 14 days. (A) Gene and guide level analysis of published core essential genes (HART_CEGv2, purple) and non-essential genes (HART_NEG, green) at screening endpoint compared to T0 (Hart et al., 2017). Guides targeting non-essential genes exhibit neutral behavior while those targeting essential genes dropout during the screen as cells expressing these guides should not be able to survive. (B) DrugZ screen analysis showing log2 fold enrichment of each gene and associated p-values; significantly enriched genes (positive Log2 Fold Change) drive resistance to the drug treatment indicating these genes potentially enhance the drug response. The top 20 hits by Drug Z P-value are labeled and highlighted.
Whole-genome screen using Edit-R Human All-in-one Lentiviral Pooled Library identifies high-confidence resistance hits in A375 cells treated with Vemurafenib
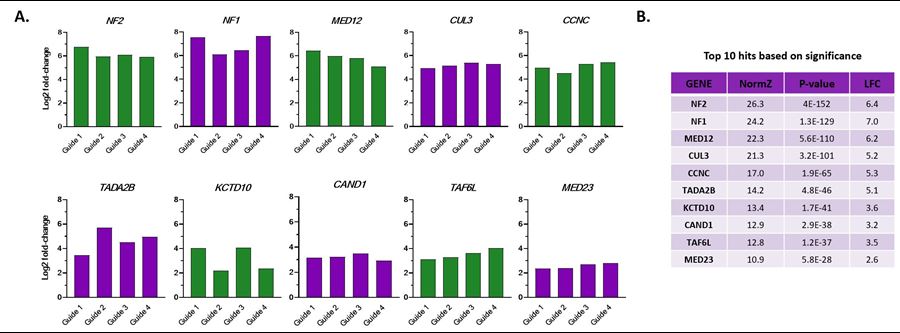
(A) DrugZ analysis from CRISPR knockout vemurafenib screening showing log2 fold enrichment of each of the guides targeting each of the top ten gene-level hits and (B) table of associated gene-level NormZ score, P-value, and Log2 Fold Change (LFC).

