Achieve screening success with pooled lentiviral libraries. High-quality pools, complete analysis tools, and validated protocols.
Highlights
- Pools of shRNA or microRNA gene families and pathways
- Customizable promoter and reporter options, including inducible promoters
- Complete workflow planning tools and protocols
- Custom human, mouse, and rat libraries available
Screen 100s or 1000s of genes without the need for costly automation
Use pooled lentiviral screens to identify genes that regulate cellular responses and signaling pathways, or to discover novel gene functions. Pooled screening libraries can consist of as few as 50 constructs up to many 1000s. In contrast to the costly automated techniques that are required in arrayed screen using individually arrayed reagents, pooled screening libraries allow the researcher to transduce and screen a population of cells within a few tissue culture dishes.
To learn more about the critical parameters of successful pooled lentiviral screening, including the conditions necessary for maintaining a high fold-representation, please download the following publication: Ž. Strezoska, A. Licon, Optimized PCR Conditions and Increased shRNA Fold Representation Improve Reproducibility of Pooled shRNA Screens. PLoS One 7, e42341 (2012).
All Horizon pooled lentiviral libraries include:
- High-quality pools provided as purified, concentrated lentiviral particles
- Choice of gene families or whole genome libraries
- Availability of custom collections, simply request a quote
- Planning tools and validated experimental and bioinformatics protocols for successful pooled lentiviral screens
Horizon products recommended in our validated Pooled Lentiviral Screening protocol:
- Optimized and validated vector-specific primer kits for
- Efficient PCR amplification of genomic DNA with minimal bias
- High-throughput multiplexed sequencing for hit identification
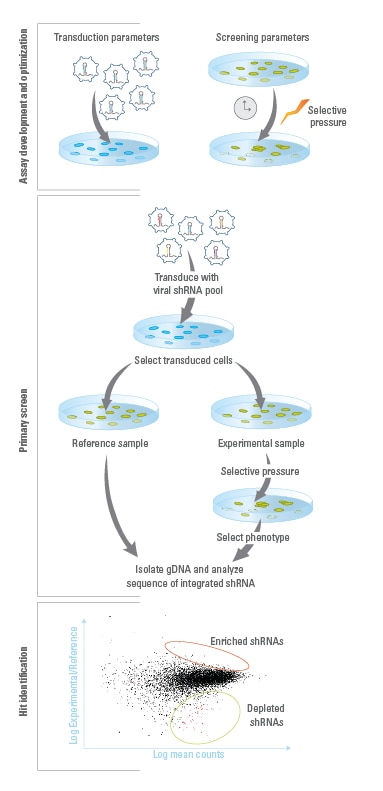
Assay Development and Optimization
Establish optimal experimental conditions, including those for a) lentiviral transduction and b) screening parameters, such as selective pressure and time between collection of reference and experimental samples.
Primary Screen
A stable population of cells expressing single integrants of constructs is created by transducing lentiviral pools at low MOIs. Transduced cells are then split into reference and experimental populations for application of a selective pressure that induces the phenotype of interest. Genomic DNA (gDNA) is then isolated from reference and experimental populations of transduced cells. Illumina-adapted primers and Phusion Hot-Start II High Fidelity DNA Polymerase are used to PCR amplify integrated construct sequences and add Illumina flow-cell binding sequences. The resulting amplicons are run on Illumina platform sequencers, using the sequencing primers provided.
Hit Identification and Follow-up
Construct sequences are identified in reference and experimental libraries. Constructs that are enriched or depleted during the screen are identified as hits, and the genes that they target are identified. Hits can be confirmed and studied further using individual constructs that can be ordered from the Dharmacon catalog collection.
-
SMARTvector Lentiviral shRNA Pooled Libraries
Constitutive shRNA expression for optimized functional analysis screens -
SMARTvector Inducible Lentiviral shRNA Pooled Libraries
Inducible shRNA expression for regulatable and controlled functional analysis screens -
shMIMIC Lentiviral microRNA Pooled Libraries
Perform functional screening of hundreds or thousands of microRNAs without high-throughput automation -
shMIMIC Inducible Lentiviral microRNA Pooled Libraries
Tight control of microRNA expression for powerful functional screening of hundreds or thousands of microRNAs. -
SMARTvector Indexing PCR and Sequencing Primer Kit
For use with SMARTvector and shMIMIC pooled libraries on Illumina systems
Select any SMARTvector lentiviral shRNA, SMARTvector Inducible Lentiviral shRNA, shMIMIC Lentiviral microRNA, shMIMIC Inducible Lentiviral microRNA, or GIPZ construct for human, mouse, or rat (where available).
- Available pool sizes are between 50 to 10,000 constructs
- Pools are provided as purified, concentrated lentiviral particles (≥ 5 x 108TU/mL for constitutive vectors and ≥ 1 x 107TU/mL for inducible vectors)
- Choose lentiviral particle quantity (minimum volume 100 µL)
- Prior to viral production, pools are analyzed for recovery and uniformity of constructs by NGS analysis
- A data file which includes construct sequences, RefSeq gene accessions, Entrez gene IDs or miRBase gene IDs, and counts per millions of mapped reads is provided
Horizon products recommended in our validated Pooled Lentiviral Screening protocol:
- Non-targeting control lentivirus for transduction optimization
- Vector-specific Indexing PCR and Sequencing Primer Kits which includes optimized and experimentally validated primers for:
- Efficient PCR amplification of genomic DNA with minimal bias and
- High-throughput multiplexed sequencing for hit identification
- Experimentally tested protocols and planning tools for successful pooled lentiviral screens
Before requesting a quote, download these invaluable tools to carefully plan your pooled lentiviral screen and calculate the amounts of components required:
- Pooled Lentiviral Screening Libraries Technical Manual
- Laboratory Protocols and Calculation Tracking Worksheet
- Bioinformatics documentation
Important Notice
The pooled lentiviral screening libraries and reagents are solely for internal research use (as set forth in the Product Terms and Conditions) in laboratories where the containment measures stated below and in applicable laws and regulations are met. Products may not be used for diagnostic, therapeutic or other commercial purposes and may not to be administered to humans for any purpose or to animals for therapeutic purposes. All pooled lentiviral screening libraries provided as lentiviral particles are replication-incompetent, self-inactivating (SIN) and non-pathogenic (do not cause infectious human disease).
Any investigator who purchases lentiviral particle products is responsible for consulting with their institution's health and biosafety personnel for specific guidelines on the handling of lentiviral vector particles. Furthermore, each investigator is fully responsible for obtaining the required permissions for research using and the acceptance of replication-incompetent SIN lentiviral vectors and replication-defective lentiviral particles into their local jurisdiction and institution.
