- Gene modulation
- RNA interference
- siRNA solutions by Dharmacon™
- ON-TARGETplus siRNA
ON-TARGETplus siRNA
siRNA designed and modified for greater specificity
- NEW! Discover Dharmacon™ ON-TARGETplus™ 2.0 siRNA - our newest version with modern designs, product updates, and the latest transcriptome alignment to maximize specificity and transcript isoform coverage
- Guaranteed gene silencing
- Patented modifications to reduce off-targets
- Available as individual siRNA or in SMARTpool™ format – for human, mouse or rat

ON-TARGETplus siRNA
1Start Here
2Choose
Knockdown your target gene function with confidence
The patented modification pattern for specificity, combined with the SMARTselection algorithm for efficient, guaranteed target gene silencing, makes Dharmacon ON-TARGETplus siRNA the premium choice for optimal knockdown and reduced off-targets.
Available as pre-designed, genome-wide reagents for human, mouse and rat.
- For the most up-to-date designs explore ON-TARGETplus 2.0 siRNA with continuous transcriptome alignment to maximize specificity and transcript isoform coverage
- Off-targets reduced by up to 90% compared to unmodified siRNA
- Guaranteed silencing with our SMARTpool™ format and 3 of 4 individual siRNAs (see Guarantee tab)
- Sequence information provided with siRNA purchase
ON-TARGETplus technology
A two-stranded mechanism requires a two-stranded solution.
Dharmacon scientists and collaborators demonstrated in 2006 (see Reference 1) that siRNA off-targets are mediated by antisense seed-region interactions, initiating the development of a dual-strand modification pattern:
- Sense strand is modified to prevent interaction with RISC and favor antisense strand uptake
- Antisense strand seed region is modified to destabilize off-target activity and enhance target specificity
Seed-region analysis on siRNA designs reduces miRNA-induced off-targets
A landmark publication (see Reference 2) from the Dharmacon research group was the first to experimentally demonstrate the key role of the seed region in mediating off-targets. A subsequent 2008 paper (see Reference 3) showed the importance of seed frequency in the 3' UTR as an indicator of its likelihood to cause off-targets. These principles were subsequently applied to our siRNA designs to improve specificity:
- Design filters eliminate common seed regions likely to cause miRNA-like off-targets
- Seed frequency analysis for siRNA designs minimize off-target effects
Product formats
- SMARTpool: A mixture of 4 siRNA provided as a single reagent; providing advantages in both potency and specificity.
- Set of 4: A convenient option for purchasing aliquots of all 4 individual siRNAs targeting a single gene.
- Individual siRNAs: For the most precise knockdown of specific transcript isoforms
Components for an RNAi experiment using synthetic siRNA
- ON-TARGETplus siRNA
- Appropriate positive and non-targeting controls
- DharmaFECT transfection reagent or electroporation for delivery
- siRNA buffer and/or RNase-free water for resuspension of siRNA.
Note: You can order guide RNA above, with the option to add any of these additional components directly to your cart.
Order quantity guidelines
ON-TARGETplus reagents are routinely used at 5 to 25 nM concentration. The calculations below, based on 25 nM, are for estimation purposes only and assume no loss from pipetting.
| Approximate # reactions (wells) at 25 nM siRNA concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| nmol | 96-well plate (100 µL total reaction volume) | 24-well plate (500 µL total reaction volume) | 12-well plate (1000 µL total reaction volume) |
| 1 | 400 | 80 | 40 |
| 2 | 800 | 160 | 80 |
| 5 | 2000 | 400 | 200 |
| 10 | 4000 | 800 | 400 |
| 20 | 8000 | 1600 | 800 |
Custom siRNA design
Design and order custom siRNA sequences using our siDESIGN center.
Our siRNA knockdown guarantee
ON-TARGETplus siRNA reagents (SMARTpool and three of four individual siRNAs) are guaranteed to silence target gene expression by at least 75% at the mRNA level when demonstrated to have been used under optimal delivery conditions (confirmed using validated positive control and measured at the mRNA level 24 to 48 hours after transfection using 100 nM siRNA).
Note: Most ON-TARGETplus siRNA products are highly functional at 5 to 25 nM working concentration.
Complete your knockout experiment by adding these supporting reagents to your order
ON-TARGETplus siRNA controls
Validated positive controls and non-targeting negative controls utilizing patented modifications for optimal specificity. Available as pools or single siRNAs. On-TARGETplus control siRNAs and pools are produced with the patented ON-TARGETplus modification pattern for optimal specificity. They are recommended as controls for any siRNA experiment due to their minimized off-target effects.
Our panel of non-targeting controls permits assessment of potential non-specific effects, to find the optimal negative control for your cell type, and your assay. Pooled siRNA controls are recommended for further reduction of off-targets, and for use with SMARTpool siRNA reagents.
Select a species-specific positive control to silence an expressed housekeeping gene in your experimental cell type.
| ON-TARGETplus Positive Control Reagents | Species | Catalog Number |
|---|---|---|
| ON-TARGETplus Cyclophilin B Control siRNA | Human | D-001820-01 |
| Mouse | D-001820-02 | |
| Rat | D-001820-03 | |
| ON-TARGETplus Cyclophilin B Control Pool | Human | D-001820-10 |
| Mouse | D-001820-20 | |
| Rat | D-001820-30 | |
| ON-TARGETplus GAPD Control siRNA | Human | D-001830-01 |
| Mouse | D-001830-02 | |
| Rat | D-001830-03 | |
| ON-TARGETplus GAPD Control Pool | Human | D-001830-10 |
| Mouse | D-001830-20 | |
| Rat | D-001830-30 | |
| ON-TARGETplus Negative Control Reagents | Species | Catalog Number |
| ON-TARGETplus Non-targeting siRNAs | Human, Mouse, Rat | D-001810-0X |
| ON-TARGETplus Non-targeting Pool | Human, Mouse, Rat | D-001810-10 |
Transfection reagents
DharmaFECT transfection reagents are optimized for improved delivery and reduced toxicity. The optimal DharmaFECT reagent for your experiment will depend on your Cas9 nuclease source and your cell type.
Order quantity guidelines
ON-TARGETplus reagents are routinely used at 5 to 25 nM concentration. The calculations below, based on 25 nM, are for estimation purposes only and assume no loss from pipetting.
| Approximate # reactions (wells) at 25nM siRNA concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| nmol | 96-well plate (100 µL total reaction volume) | 24-well plate (500 µL total reaction volume) | 12-well plate (1000 µL total reaction volume) |
| 1 | 400 | 80 | 40 |
| 2 | 800 | 160 | 80 |
| 5 | 2000 | 400 | 200 |
| 10 | 4000 | 800 | 400 |
| 20 | 8000 | 1600 | 800 |
ON-TARGETplus modifications reduce the overall number of off-targets and pooling reduces them even further
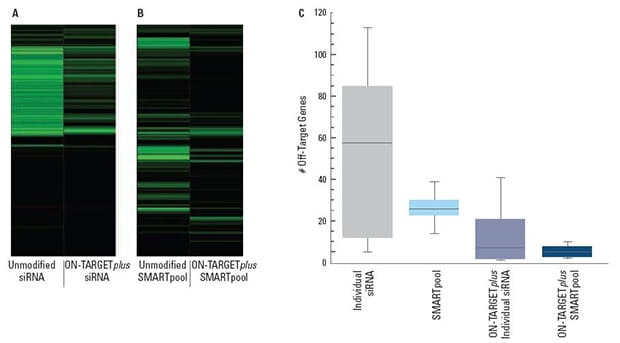
Panels (A) and (B) are representative examples of off-target signatures with and without application of ON-TARGETplus modifications to (A) a single siRNA and (B) a SMARTpool reagent. Green bars indicate genes with 2-fold or more reduction of expression when treated with the indicated siRNA reagent.The ON-TARGETplus modifications reduced the off-targets when compared to unmodified siRNA. Pooling of siRNA and the ON-TARGETplus modification pattern independently, and in combination, provide significant reduction in off-target gene silencing. Panel (C) represents quantitation of off-targets (down-regulated by 2-fold or more) induced by the indicated siRNA reagents targeting 10 different genes (4 siRNAs per gene or a single SMARTpool reagent). Off-targets were quantified using microarray analysis (Agilent) then compiled. Each shaded box represents the middle 50% of the data set. Horizontal line in box: Median value of the data set. Vertical bars: minimum and maximum data values.
False phenotypes due to off-targets are alleviated by ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool reagents while target gene knockdown is maintained
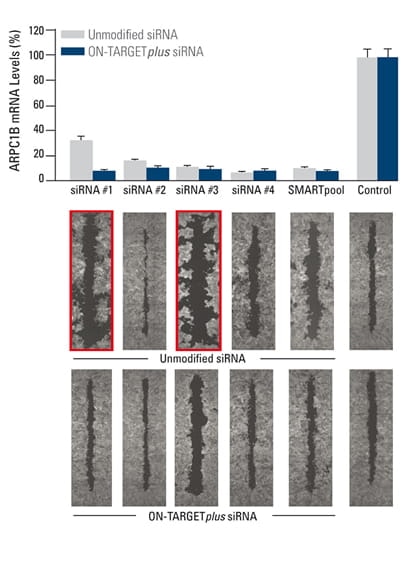
The effect of silencing ARPC1B on cell migration was studied in a breast cancer cell line. A monolayer of cells was uniformly scraped and the rate of cell migration to close the scrape (wound healing) was evaluated. Both unmodified and ON-TARGETplus siRNA reagents induced potent target knockdown. Inconsistent phenotypes due to off-target effects (red outline), were observed for cells transfected with unmodified individual siRNAs. The unmodified SMARTpool improved the false phenotype considerably, while the ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool significantly reduced off-target effects to produce a consistent phenotype.
In collaboration with Kaylene Simpson, Laura Selfors, and Joan Brugge, Harvard Medical School.
Only the ON-TARGETplus modification pattern addresses both siRNA strands for premium silencing
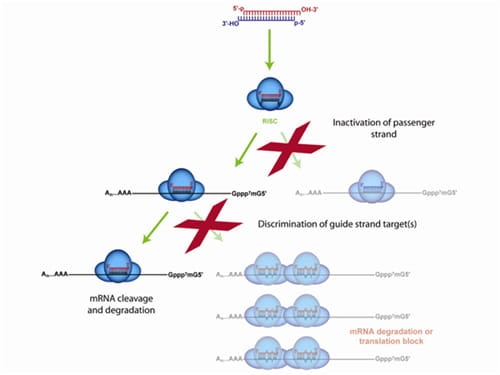
The ON-TARGETplus dual-strand chemical modification begins with the sense (passenger) strand being blocked from RISC uptake to favor antisense (guide) strand loading and reduce passenger strand-induced off-targets. However, the majority of siRNA off-targets are driven by the seed region of the guide strand. ON-TARGETplus is modified within its seed region to destabilize miRNA-like activity and improve specificity to the desired target for potent knockdown.
siRNA designs with low-frequency seed regions ensure fewer off-targets
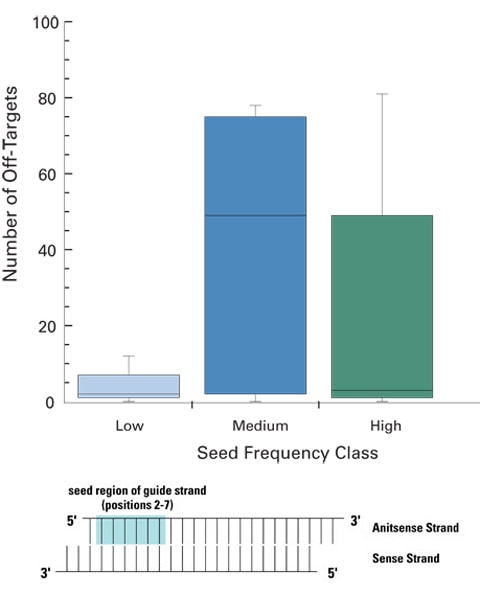
ON-TARGETplus siRNA designs leverage sophisticated bioinformatics to reduce the likelihood of miRNA-like off-targets from high-frequency or highly conserved miRNA seed regions. siRNAs with low seed frequency have a significantly lower number of off-targets than siRNAs with medium or high frequency seeds. Five siRNAs with low, medium, or high frequency seed regions were transfected into HeLa cells and their associated off-target signatures assessed via global expression profiling (Agilent 22K platform). siRNA sequences were constant at positions 1 and 8-19, only the seed regions (positions 2-7) were altered.
Low frequency seeds: < 350 occurrences in the HeLa transcriptome
Medium frequency: 2500-2800 occurrences
High frequency: >3800 occurrences
ON-TARGETplus siRNA dual-strand modification pattern reduces off-targets
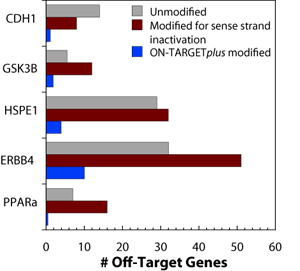
Off-target effects have been shown to be primarily driven by antisense strand seed activity. Therefore, sense strand inactivation alone does not decrease the total number of off-target genes.
ON-TARGETplus modifications account for both strands:
- Sense strand is modified to prevent interaction with RISC and favor antisense strand uptake
- Antisense strand seed region is modified to minimize seed-related off-targeting
The ON-TARGETplus modification pattern dramatically reduces off-targets. Off-target effects induced by the indicated siRNAs were quantified using microarray analysis. For each target, three different siRNAs were used: unmodified, sense strand-inactivated, and ON-TARGETplus-modified. Data shown represents genes down-regulated by two-fold or more. HEK293 cells were transfected with 100 nM siRNA using 0.2 μL of DharmaFECT 1. Data was analyzed at 24 hours.
- A. L. Jackson et al., Position-specific chemical modification increases specificity of siRNA-mediated gene silencing. RNA. 12(7), 1197-1205 (July 2006).
- A. Birmingham et al., 3'-UTR seed matches, but not overall identity, are associated with RNAi off-targets. Nature Methods. 3(3), 199-204 (March 2006).
- E. M. Andersonet al., Experimental validation of the importance of seed complement frequency to siRNA specificity. RNA. 14(5), 853-861 (May 2008).
Application notes
Product inserts
Protocols
Safety data sheets
Selection guides
Related Products
The most broadly applicable DharmaFECT formulation for optimal siRNA or microRNA transfection into a wide range of cell types for successful RNAi experiments
Catalog ID:T-2001-01
Unit Size:0.2 mL
$116.00
A validated positive control pool of four siRNAs targeting the cyclophilin B (PPIB) gene in human, mouse, or rat. Includes patented ON-TARGETplus modifications to minimize off-target effects. Useful for determination of optimal RNAi conditions.
Catalog ID:D-001820-10-05
Unit Size:5 nmol
$269.00
Validated positive control pool of four siRNAs targeting GAPD gene in human, mouse, or rat. Includes patented ON-TARGETplus modifications to minimize off-target effects. Useful for determination of optimal RNAi conditions.
Catalog ID:D-001830-10-05
Unit Size:5 nmol
$269.00
Negative control pool of four siRNAs designed and microarray tested for minimal targeting of human, mouse or rat genes. ON-TARGETplus modifications reduce potential off-targets. Recommended for determination of baseline cellular responses in RNAi experiments.
Catalog ID:D-001810-10-05
Unit Size:5 nmol
