- CRISPR activation reagents
- CRISPRa lentiviral dCas9-VPR reagents
CRISPRmod CRISPRa lentiviral dCas9-VPR reagents
Lentiviral dCas9-VPR vectors for robust gene activation in a broad range of relevant cell types
Purified lentiviral particles or plasmid DNA for generation of stable dCas9-VPR nuclease-expressing cell populations
Inquire for pricing on larger volumes

CRISPRa dCas9-VPR lentiviral particles express a human codon-optimized version of the nuclease-deactivated Cas9 gene, fused to three transcriptional activators (VP64, p65 and Rta), and two nuclear localization signals (NLS). When paired with a well-designed guide RNA that targets a gene near a promoter region, the gene's native transcription start site is activated.
Review our CRISPRa application page to get an overview of the technology.
Highlights
- Generate your own stable "CRISPRa ready" dCas9-VPR-expressing cell line.
- Concentrated, purified lentiviral particles are ready for immediate transduction (minimum ≥1×107 TU/mL functional titer, by qPCR).
- Also available as certified endotoxin-free plasmid DNA for direct transfection into a packaging cell line and production of your own lentiviral particles.
- Blasticidin resistance gene offers easy cell population selection or for clonal expansion of individual cells.
- Choose from one of three different promoters for optimum expression in your cells of interest (see options below).
Requirements for a CRISPRa experiment using dCas9-VPR lentiviral particles
- CRISPRa dCas9-VPR lentiviral particles.
- CRISPRa lentiviral sgRNA for your target gene (see Workflow tab).
Not all RNA pol II promoters are equally active in different cellular environments
The activity of any given promoter controlling the transcription of dCas9-VPR can differ greatly from one biological context to another, resulting in variable dCas9-VPR expression levels and thus varying levels of gene activation. Choosing an optimal promoter for your cell line will be important for robust gene overexpression.
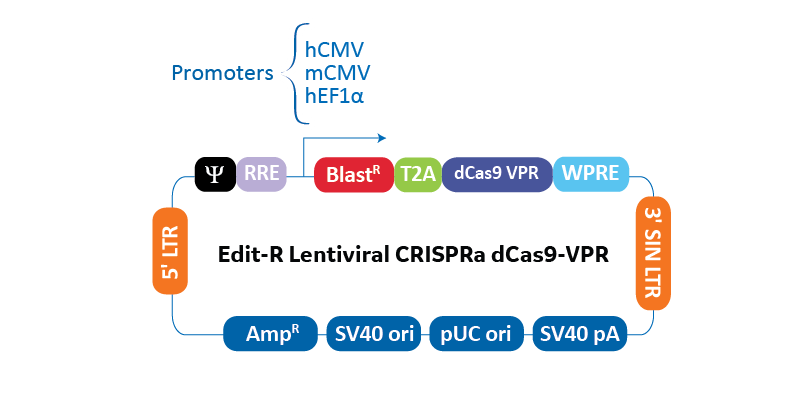 SMARTchoice promoter options for expressing dCas9-VPR
SMARTchoice promoter options for expressing dCas9-VPR
| Promoter | Description |
|---|---|
| hCMV | human cytomegalovirus immediate early promoter |
| mCMV | mouse cytomegalovirus immediate early promoter |
| hEF1α | human elongation factor 1 alpha promoter |
CRISPRa workflow diagram with stable dCas9-VPR expression
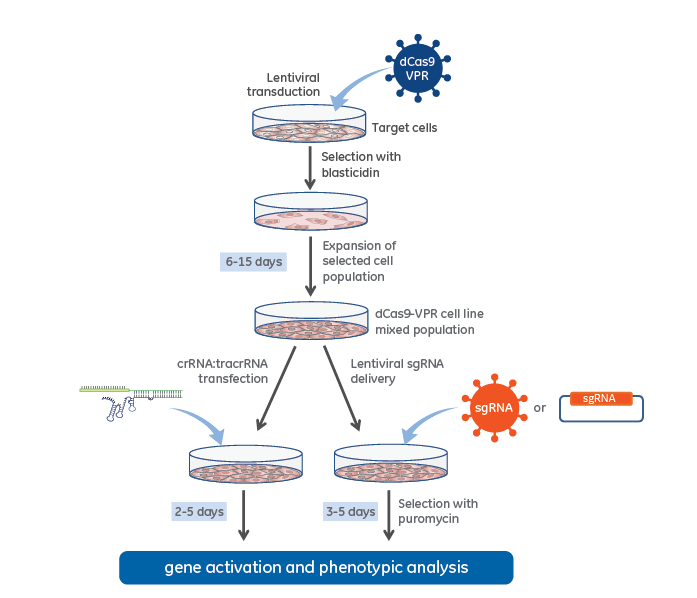
CRISPR activation workflow with lentiviral dCas9-VPR and synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA (left side) or Lentiviral expressed sgRNA (right side).
CRISPRa plasmid co-transfection workflow
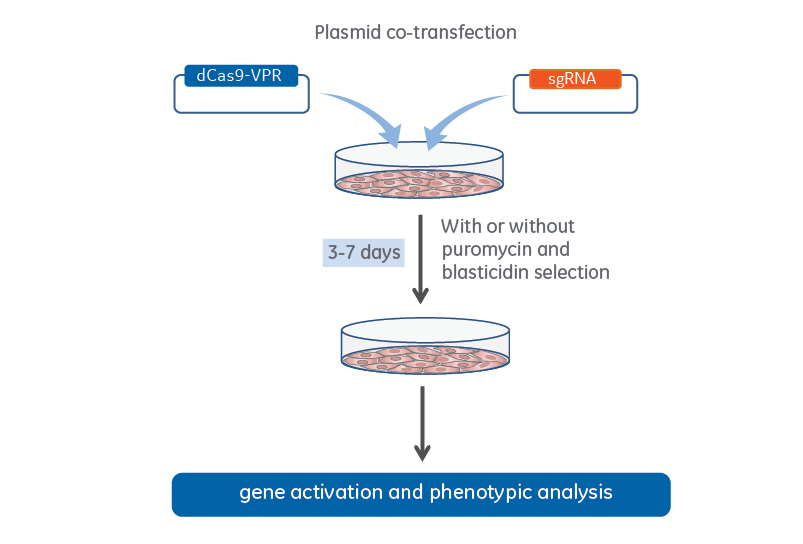
CRISPRa workflow for plasmid co-transfection of lentiviral dCas9-VPR and expressed sgRNA.
CRISPRa gene activation fold depends on the endogenous gene expression level
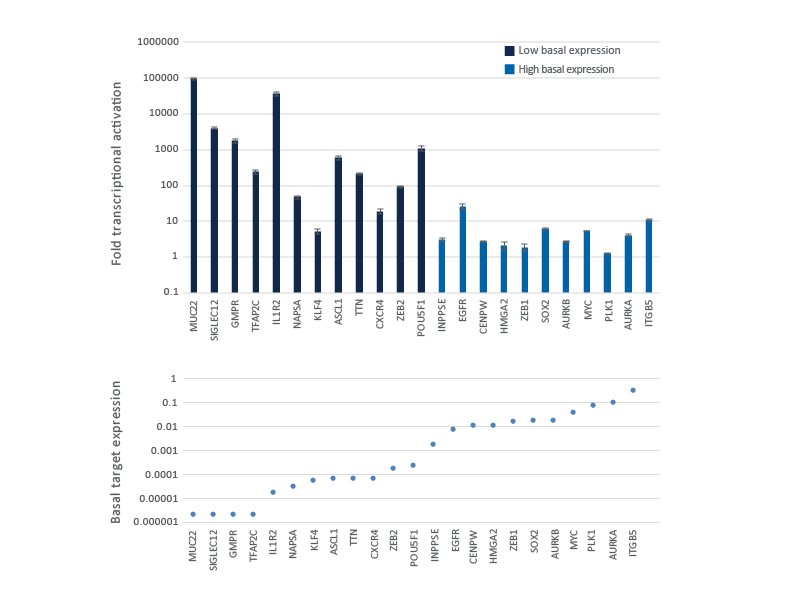
Genes with low or no basal expression are easier to activate to a robust level, while genes already expressed at high level are more difficult to further over-express. U2OS-dCas9-VPR stable cells were plated at 10,000 cells/well and transfected using DharmaFECT 4 Transfection Reagent with CRISPRa synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA pools (25 nM) targeting 23 genes with different basal level of expression. Cells were harvested 72 hours post-transfection and the relative gene expression was measured using RT-qPCR. The CRISPRa-mediated fold transcriptional activation is shown in the upper graph where the genes are ordered from low to high level of basal transcript expression in samples treated with NTC control and is shown in the lower graph as basal target gene expression (compared to GAPDH control).
CRISPRa gene activation is observed at 24 hours and peaks at 48-72 hours
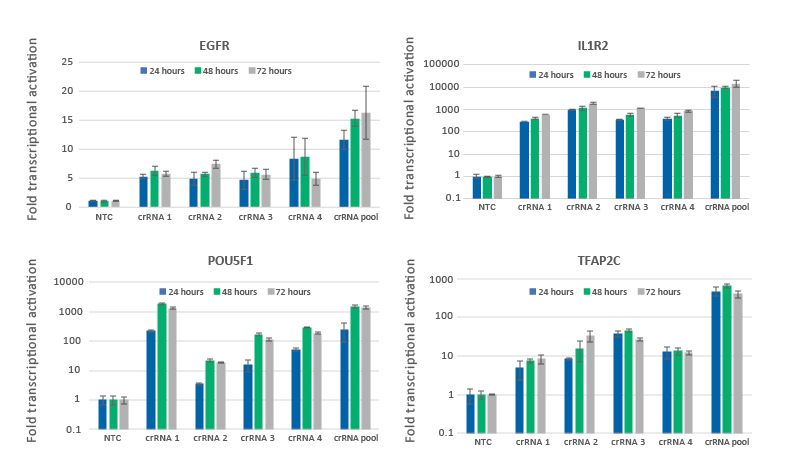
U2OS-dCas9-VPR stable cells were plated at 10,000 cells/well and transfected using DharmaFECT 4 Transfection Reagent with CRISPRa synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA targeting EGFR, IL1R2, POU5F1 or TFAP2C. Four CRISPRa crRNAs were used either individually or pooled (to a total concentration of 25 nM). Cells were harvested at 24, 48, and 72 hours post-transfection and the relative gene expression was measured using RT-qPCR. The relative expression of each gene was calculated with the Cq method using GAPDH as the housekeeping gene and normalized to a non-targeting control.
LentiBOOST Lentivirus Transduction Enhancer is a uniquely formulated transduction reagent that can be used with or without lentivirus spinfection in order to increase successful viral transduction events while preserving cell viability. Especially critical for preserving precious primary cells from patient cohorts, or, for engineering complex animal models; improving transduction efficiency can save time and costs by increasing the success of each editing/transduction step, or, even avoid the loss of irreplaceable samples. Additionally, LentiBOOST technology is already used in the manufacturing of a number of clinical stage therapies providing the opportunity to demonstrate improved workflow applicability to the clinic.
LentiBOOST can be purchased through the Dharmacon Reagents catalog.
To learn more about LentiBOOST technology visit the Revvity LentiBOOST webpage.
Supporting Data
Improved CD8+ T-cell SMARTvector™ shRNA lentiviral system transduction using LentiBOOST™ Lentivirus Transduction Enhancer
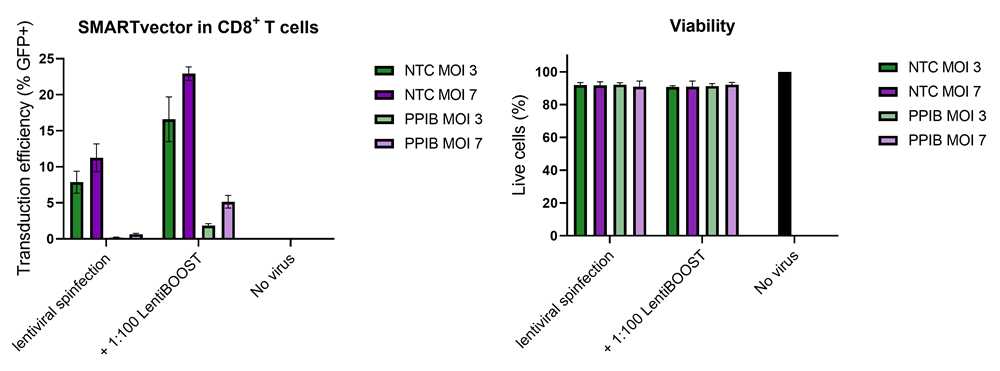
100,000 primary human CD8+ T cells were transduced with either 30,000 (MOI 3, green) or 70,000 (MOI 7, purple) TUs of SMARTVector™ mCMV tGFP Lentiviral Control Particles targeting either NTC or PPIB along with 1:100 LentiBOOST transduction enhancer. Cells were centrifuged at 800 x g for one hour at 32 °C followed by a four hour incubation prior to removal of lentiviral particles and transduction enhancer. Transduction efficiency (%GFP+ out of live cells) and viability were determined 5 days post-transduction by flow cytometry. The addition of LentiBOOST technology markedly improved transduction efficiencies without significantly impacting cell viability.
Improved CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell Edit-R™ All-in-one sgRNA/Cas9 lentiviral system transduction using LentiBOOST™ Lentivirus Transduction Enhancer
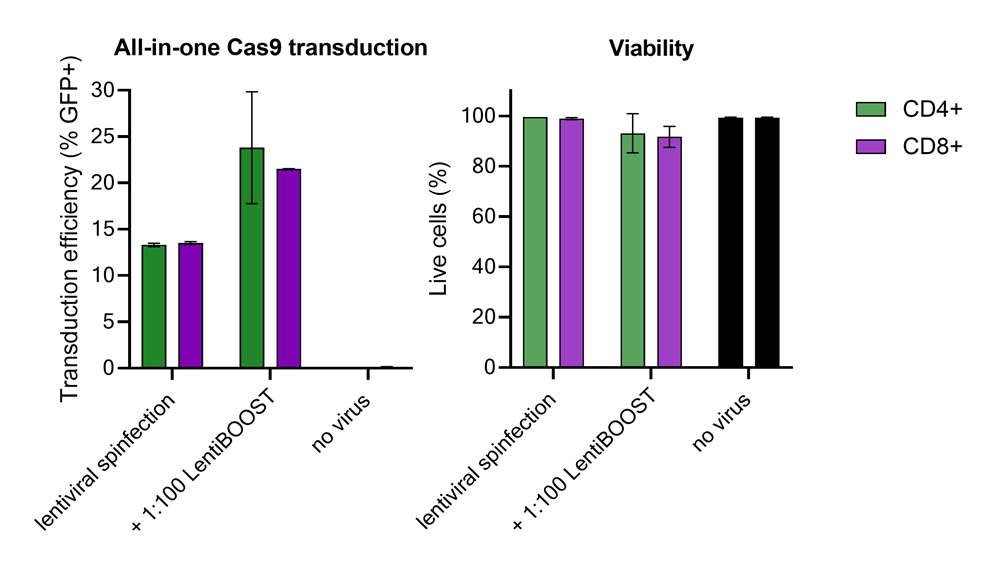
100,000 primary human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from two donors were transduced with 250,000 TUs of Edit-R GFP Delivery controls mCMV along with 1:100 LentiBOOST transduction enhancer. Cells were centrifuged at 800 x g for one hour at 32 °C followed by an overnight incubation prior to removal of lentiviral particles and transduction enhancer. Transduction efficiency and viability were determined 72 hours post-transduction by flow cytometry. The addition of LentiBOOST technology markedly improved transduction efficiencies without significantly impacting cell viability.
Improved transduction of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) with the Strict-R™ Inducible CRISPRa lentiviral system transduction using LentiBOOST™ Lentivirus Transduction Enhancer

10,000 WTC hiPS cells were transduced with either 20,000 (MOI 2, green) or 40,000 (MOI 4, purple) TUs of Strict-R™ Inducible EGFP dCas9-VPR Lentiviral Particles along with 1:100 LentiBOOST transduction enhancer. Cells were centrifuged at 800 x g for one hour at 32 °C followed by an overnight incubation prior to removal of lentiviral particles and transduction enhancer. Transduction efficiency and viability were determined 72 hours post-transduction by flow cytometry. The addition of LentiBOOST markedly improved transduction efficiencies without significantly impacting cell viability.
Quick protocols
Safety data sheets
Selection guides
Related Products
LentiBOOST transduction enhancer can increase successful viral transduction in challenging to transduce cells, or, complex cellular engineering work; while preserving cell viability and minimizing the amount of viral particles required for your experiment. LentiBOOST technology is actively used in the production of clinical stage lentivirally delivered therapies, including some approved therapies, providing a direct path to therapeutic applicability for your research studies. Tested with Dharmacon Lentiviral reagents.
Validated CRISPRa lentiviral sgRNA positive controls for optimization of experimental conditions and quantification of gene activation efficiency.
Predesigned CRISPRa lentiviral sgRNAs for highly efficient gene activation in human and mouse models; available as glycerol stocks and high-titer purified particles.
Lentiviral sgRNA constructs bioinformatically designed and validated to not target any gene in human or mouse genomes.
