- CRISPR activation reagents
- dCas9-VPR mRNA
CRISPRmod CRISPRa dCas9-VPR mRNA
A DNA-free option for dCas9-VPR expression
Purified dCas9-VPR mRNA for co-transfection or electroporation with synthetic CRISPRa crRNA for gene activation
Inquire for pricing on larger volumes

CRISPRa dCas9-VPR mRNA expresses a human codon-optimized version of the nuclease-deactivated Cas9 gene, fused to three transcriptional activators (VP64, p65 and Rta), and two nuclear localization signals (NLS). When paired with a well-designed guide RNA that targets a gene near a promoter region, the gene's native transcription start site is activated.
Review our CRISPRa application page to get an overview of the technology.
Highlights
- No need to generate a stable dCas9-VPR-expressing cell line.
- Simply co-transfect CRISPRa synthetic sgRNA or crRNA:tracrRNA and dCas9-VPR mRNA using DharmaFECT Duo transfection reagent or co-electroporate into cells.
- Straightforward enrichment options – choose to co-express EGFP or puromycin resistance (see supporting data).
- Translation ready mRNA eliminates the need for optimal promotor selection.
CRISPRa gene activation by electroporation of dCas9-VPR mRNA and synthetic guide RNA
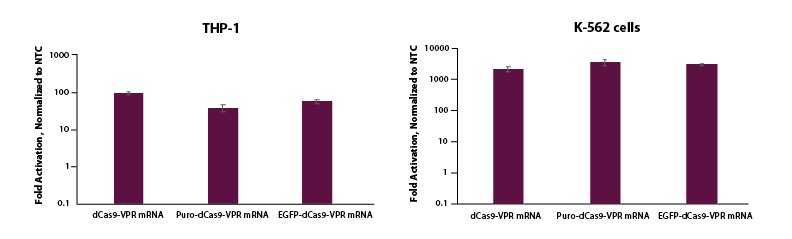
THP-1 and K-562 cells were electroporated using the Lonza 2b system with either dCas9-VPR mRNA (5 µg, Cat #CAS12024), Puro dCas9-VPR mRNA (5 ug, Cat #CAS12026) or EGFP dCas9-VPR mRNA (5 ug, Cat #CAS12025), synthetic tracrRNA (25 nM, Cat #U-002005-05), and pooled CRISPRa crRNA targeting TTN (5 uM, Cat #P-005395-01-0005) or non-targeting control (NTC, 25 nM, Cat #U-009500-10-05). Cells were harvested at 48 hours post-transfection and total RNA was isolated. Relative gene expression was measured using RT-qPCR. The relative expression of each gene was calculated with the Cq method using GAPDH as the housekeeping gene and normalized to a non-targeting control.
FACS can be used to select for cells with EGFP dCas9-VPR mRNA and enrich for gene activation
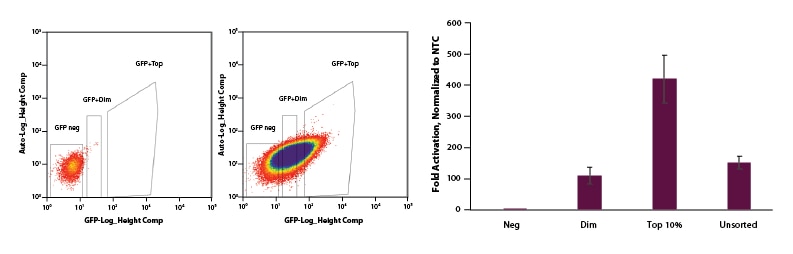
U2OS cells were plated at 200,000 cells per well in clear 6-well plates. After 24 hours, cells were co-transfected with CRISPRa EGFP dCas9-VPR mRNA (2 µg, Cat #CAS12025), synthetic tracrRNA (25 nM, Cat #U-002005-05), and pooled CRISPRa crRNA targeting IL1R2 (25 nM, Cat #P-007960-01-0005) or Non-targeting control (NTC, 25 nM, Cat #U-009500-10-05) using DharmaFECT Duo (2 µg/well, Cat #T-2010-01). At 24 hours post-transfection, cells were trypsinized and FACS was performed and cells were sorted into three categories: Negative, Dim, and Top 10%. Cells were replated in 6-well dishes and allowed to recover. After 24 hours, total RNA was isolated and relative gene expression was measured using RT-qPCR. The relative expression of each gene was calculated with the Cq method using GAPDH as the housekeeping gene and normalized to a non-targeting control. The negative population of cells sorted shows no activation. The Dim and Unsorted populations both showed ~120-fold activation and our Top 10% population resulted in 450-fold activation.
Puromycin resistance can be used to select for cells with Puro dCas9-VPR mRNA and enrich for gene activation

U2OS cells were plated at 200,000 cells per well in clear 6-well plates. After 24 hours, cells were co-transfected with Puro dCas9-VPR mRNA (2 µg, Cat #CAS12026), synthetic tracrRNA (25 nM, Cat #U-002005-05), and pooled CRISPRa synthetic crRNA targeting either POU5F1 (25 nM Cat #P-019591-01-0005), IL1R2 (25 nM, Cat #P-007960-01-0005), TFAP2C (25 nM, Cat #P-005238-01-0005), TTN (25 nM, Cat #P-005395-01-0005) or non-targeting control (NTC, 25 nM, Cat #U-009500-10-05) using DharmaFECT Duo (2 µg/well, Cat #T-2010-01). At 24 hours post-transfection, 2 µg/ml of puromycin growth media was added to the cells and a duplicate plate received normal growth media. At 48 hours post-transfection a crystal violet assay was performed and images captured to assess viability and total RNA was isolated. Relative gene expression was measured using RT-qPCR. The relative expression of each gene was calculated with the Cq method using GAPDH as the housekeeping gene and normalized to a non-targeting control. For all genes tested, we observed 3- to 5-fold enrichment of activation when compared to unselected samples.
Efficient gene activation with dCas9-VPR mRNA and target sgRNA
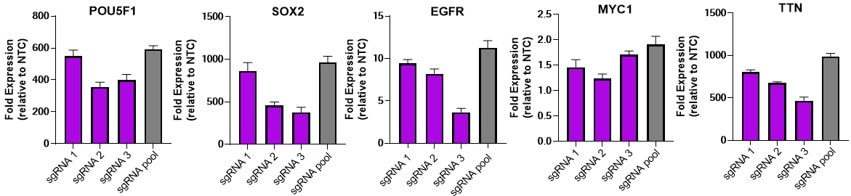
U2OS were plated at 10,000 cells/well and transfected using DharmaFECT Duo (0.15uL/well) Transfection Reagent with 25nM individual or pooled CRISPRa synthetic single guide RNA (sgRNA) targeting POU5F1, SOX2, EGFR, MYC1 or TTN and 200 ng / well of CRISPRmod CRISPRa dCas9-VPR mRNA. Cells were harvested at 72 hours post-transfection and gene expression was assessed using RT-qPCR. Relative fold transcriptional activation for each gene was calculated with the Cq method using beta-actin as the housekeeping gene and normalized to an experiment using non-targeting control sgRNA.

