- Dharmacon Screening libraries
- CRISPRmod CRISPRa synthetic crRNA libraries
CRISPRmod CRISPRa synthetic crRNA libraries
Something innovative and game-changing is on the horizon! We’re thrilled to announce brand-new CRISPRa sgRNA libraries that are set to streamline your CRISPRa screening. To learn more, stay up to date and receive a consult on the newest library offerings contact us.

CRISPRmod CRISPRa synthetic crRNA arrayed libraries enable one-gene-per-well investigation using high-content assays to answer in-depth biological questions. Further your drug discovery, pathway analysis, or disease progression studies with CRISPR activation screening.
Don't see your gene family of choice? Upload your own gene to our Cherry-pick Library Plater for a fully customized CRISPRa screening library.
Highlights of CRISPRa crRNA libraries:
- Available as four individual crRNAs per gene or a pool of four crRNAs to provide highly effective transcriptional activation (see Supporting Data tab)
- crRNA pools provide robust activation while reducing costs, storage, and handling of libraries compared to working with four individual crRNAs
- Algorithm-generated designs (published by Horlbeck, et. al.1) demonstrate robust transcript activation (See References tab)
- Chemically modified CRISPRa crRNAs and tracrRNA provide additional stability against nuclease degradation and improve overall performance
- Conveniently arrayed in 96- or 384-well plates and offered as gene family collections. Echo-qualified 384-well plates are available upon request
Required components for an CRISPRa gene activation experiment using synthetic crRNA:
- A lentiviral expression plasmid or lentiviral particles for dCas9-VPR2; a mammalian codon-optimized S. pyogenes deactivated Cas9 fused to VPR activation domains
- CRISPRa crRNA are also compatible with SunTag technology3
- trans-activating CRISPR RNA (tracrRNA)
| Human CRISPRa crRNA Libraries | # genes (approximate) | Catalog # (Pool/Set of 4) |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Cycle Regulation | 169 | GP/GC-103205-xx |
| Cytokine Receptors | 110 | GP/GC-104005-xx |
| Deubiquitinating Enzymes | 94 | GP/GC-104705-xx |
| DNA Damage Response | 240 | GP/GC-106005-xx |
| Drug Targets | 3686 | GP/GC-104650-xx |
| Druggable Genome* | 8422 | GP/GC-104605-xx |
| Epigenetics | 835 | GP/GC-106105-xx |
| G Protein-coupled Receptors | 390 | GP/GC-103605-xx |
| Genome | 19,127 | GP/GC-105005-xx |
| Ion channels | 417 | GP/GC-103805-xx |
| Membrane Trafficking | 140 | GP/GC-105505-xx |
| Nuclear Receptors | 52 | GP/GC-103405-xx |
| Phosphatases | 254 | GP/GC-103705-xx |
| Proteases | 576 | GP/GC-105105-xx |
| Protein Kinases | 746 | GP/GC-103505-xx |
| Transcription Factors | 1580 | GP/GC-105805-xx |
| Tyrosine Kinases | 90 | GP/GC-103105-xx |
| Ubiquitin Enzymes | 738 | GP/GC-106205-xx |
*Druggable genome is made up of: Proteases, Protein Kinases, Phosphatases, Transcription Factors, Ubiquitin Enzymes, GPCRs, Ion Channels and Drug Targets.
Efficient transcriptional gene activation with synthetic crRNA in multiple dCas9-VPR stable cells
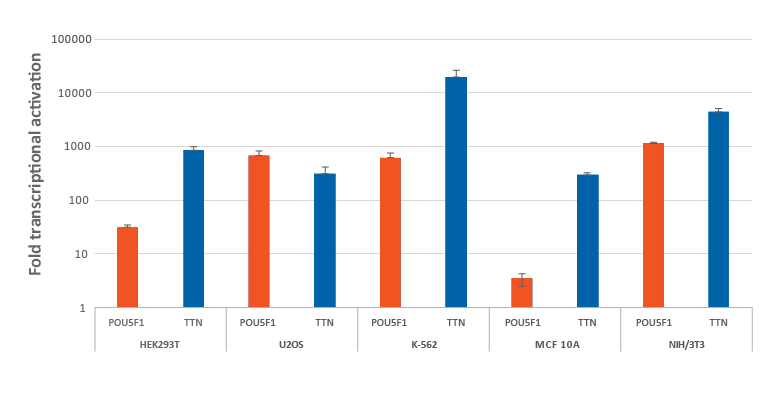
HEK293T, U2OS, MCF 10A, NIH/3T3 stably expressing integrated dCas9-VPR were plated at 10,000 cells/well and transfected using DharmaFECT Transfection Reagents with CRISPRa synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA (25 nM) targeting POU5F1 and TTN. K562 cells were electroporated with CRISPRa synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA (400 nM) targeting POU5F1 and TTN. Cells were harvested 72 hours post-transfection and the relative gene expression was measured using RT-qPCR. The relative fold transcriptional activation for each gene was calculated with the Cq method using GAPDH as the reference gene and normalized to a non-targeting control.
CRISPRa gene activation in U2OS cells is observed at 24 hours and peaks at 48-72 hours
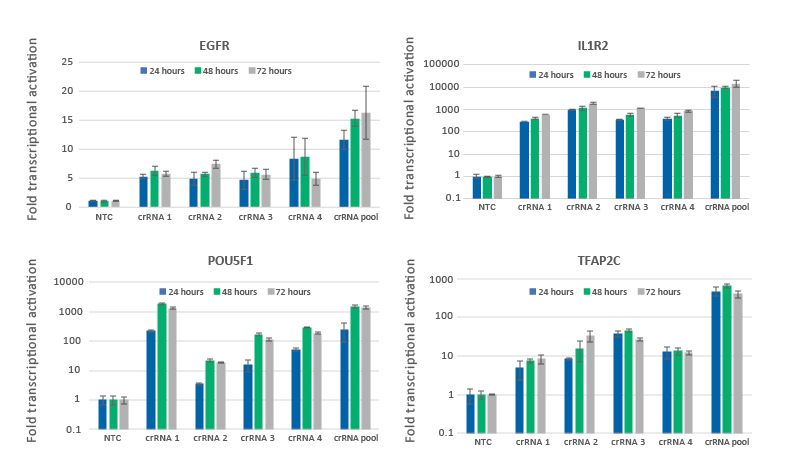
U2OS cells stably expressing integrated dCas9-VPR were plated at 10,000 cells/well and transfected using DharmaFECT 4 Transfection Reagent with CRISPRa synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA targeting EGFR, IL1R2, POU5F1 or TFAP2C. Four CRISPRa guides were used either individually or pooled (to a total concentration of 25 nM). Cells were harvested at 24, 48, and 72 hours post-transfection and the relative gene expression was measured using RT-qPCR. The relative expression of each gene was calculated with the Cq method using GAPDH as the reference gene and normalized to a non-targeting control.
CRISPRa crRNAs and pools are highly effective at 25 nM working concentration
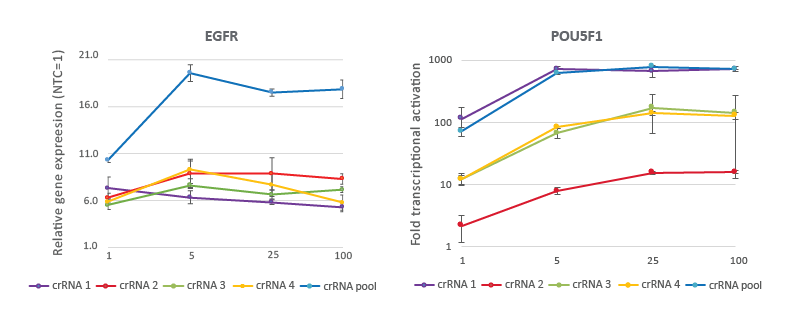
A CRISPRa dose curve targeting two different genes demonstrates that a working concentration of 25 nM achieves robust target gene activation. U2OS cells stably expressing integrated dCas9-VPR were plated at 10,000 cells/well and transfected using DharmaFECT 4 Transfection Reagent with CRISPRa synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA targeting EGFR or POU5F1. The pre-designed crRNAs were used either individually or pooled at four concentrations (1, 5, 25, 100 nM). Cells were harvested 72 hours post-transfection and the relative gene expression was calculated using RT-qPCR. The relative expression of each gene was calculated with the Cq method using GAPDH as the reference gene and normalized to a non-targeting control.
- Horlbeck MA, Gilbert LA, et. al., Compact and highly active next-generation libraries for CRISPR-mediated gene repression and activation. 2016 Sep 23;5. pii: e19760. doi: 10.7554/eLife.19760. PubMed 27661255.
-
Chavez A, Scheiman J et. al., Highly efficient Cas9-mediated transcriptional programming Nat Methods. 2015 Mar 2. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3312. 10.1038/nmeth.3312 PubMed 2573049.
-
Tanenbaum ME, Gilbert LA, et. al., A protein tagging system for signal amplification in gene expression and fluorescence imaging. Cell. 2014;159(3):635-646. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.039. PubMed 25307933
