- Gene editing
- Gene editing reagents
- Strict-R Inducible Cas9 Lentiviral System
Strict-R Inducible Cas9 Lentiviral System
Unlock precise, tunable gene knockout with the Dharmacon™ Strict-R™ Inducible Cas9 Lentiviral System. This advanced platform enables stringent, control of gene disruption with exceptional specificity and minimal off-target activity. By integrating Tet-On 3G transcriptional regulation with FKBP12-derived degron–based destabilization, the system allows inducible expression and degradation of Cas9 in response to small-molecule regulators, providing tight temporal control over genome editing activity for dynamic and time-resolved functional studies.
Dual-inducible control for precise gene knockout – How It Works
System OFF – tight regulation without inducers:
In the absence of doxycycline and Shield1, the system remains inactive. Any minimal transcriptional leakiness from the TRE3G promoter results in the production of degron-tagged Cas9, which is rapidly degraded by the proteasome, maintaining minimal background editing activity.
System ON – robust, controlled genome editing:
When doxycycline is introduced, it activates strong transcription from the TRE3G promoter. Simultaneous addition of Shield1 stabilizes the degron-tagged Cas9 protein, enabling potent and precise gene knockout in the presence of a target-specific sgRNA.
This dual-level regulation ensures stringent temporal control for gene editing experiments.
Highlights
- Achieve tight and tunable control over gene editing using small molecule–induced Cas9 expression.
- The Cas9 nuclease enables efficient, high-fidelity DNA cleavage with minimal off-target effects, ensuring precise gene disruption.
- Integration of the Tet-Degron system allows inducible expression and stabilization of Cas9 upon the addition of doxycycline and Shield1, providing dynamic, time-controlled regulation of gene editing.
- Delivered through a single lentiviral vector, the system integrates seamlessly into existing experimental workflows.
- Ideal for loss-of-function studies, functional genomics, and screening applications, this platform offers high-quality, purified lentiviral particles for direct transduction with minimal cytotoxicity (≥1 × 10⁷ TU/mL).
- Available with Hygromycin, Blasticidin selection or EGFP fluorescent reporter options for flexible experimental design.
Schematic map of the Strict-R Inducible Cas9 Lentiviral vectors
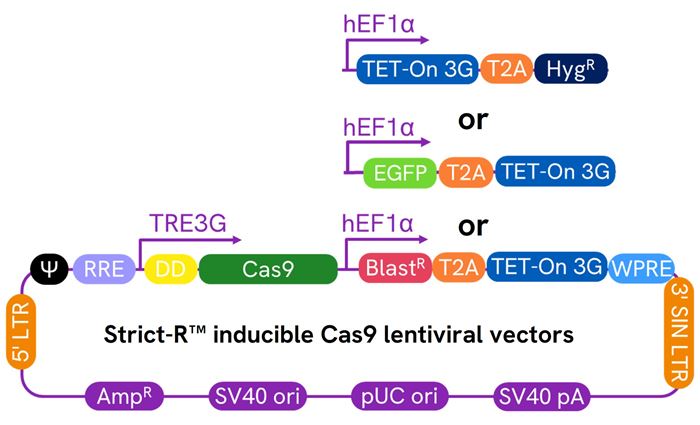
Transcriptional and post-translational control with Strict-R™ Inducible Cas9 Lentiviral System

Diagram of the Dharmacon™ Strict-R™ Inducible Cas9 Lentiviral System. In the absence of doxycycline and Shield1, the system is “OFF”. Leaky bursts of transcription from the TRE3G promoter result in the translation of Cas9 fused to a FKBP12-derived destabilizing domain (degron) that tags the protein for rapid proteasomal degradation. The addition of doxycycline induces potent transcription from the TRE3G promoter and the addition of Shield1 stabilizes the Cas9 protein thereby enabling robust target gene editing and knockout in the presence of a gene-specific sgRNA. Diagram created with BioRender.com.
Gene editing workflow using the Strict-R™ Inducible Cas9 Lentiviral System

Gene knockout workflow using the Strict-R Inducible Cas9 System
Dharmacon™ Strict-R ™ Inducible Cas9 System demonstrates minimal leakiness across cell lines
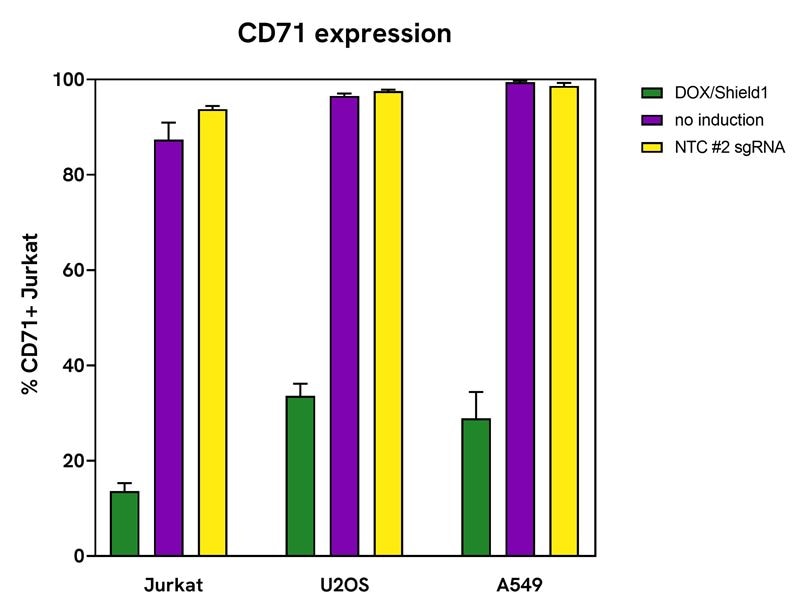
Jurkat, U2OS, and A549 cells expressing Dharmacon™ Strict-R™ Inducible Hygromycin Cas9 Lentiviral system were transduced with Edit-R lentiviral sgRNA targeting CD71 (VSGH12605-257052386) or Edit-R lentiviral sgRNA non-targeting control #2 (VSGC12626) at MOI 0.3. After 24 hours, cells were selected with 2 μg/mL puromycin for 5 days. Jurkat cells were plated in 96-well plates at 50,000 cells/well, while U2OS and A549 were plated at 20,000 cells/well. All cells were stimulated with 500 ng/mL doxycycline and 500 nM Shield1, or left untreated (‘no induction’) for 6 days. On day 6, cells were collected and stained for receptor knockout analysis by flow cytometry. The lentiviral sgRNA transduced Jurkats, U2OS or A549 were stained with FITC anti-human CD71 (1:25). Non-targeting control transduced cells were used for positive control receptor stain and isotype controls to determine positive and negative receptor gates from the untreated media condition.
Dharmacon™ Strict-R™ Inducible Cas9 Lentiviral System performs as well or better than TRE3G-only regulated Edit-R Inducible Cas9

Jurkat cells expressing Edit-R™ Inducible Cas9 (hEF1a-BlastR) Tet-only system or Dharmacon™ Strict-R™ Inducible Blasticidin- or Hygromycin-Cas9 Lentiviral System were transduced with Edit-R lentiviral sgRNA targeting CD28 (VSGH12605-256966516) or CD71 (VSGH12605-257052386) or Edit-R lentiviral sgRNA non-targeting control #2 (VSGC12626) at MOI 0.3. After 24 hours, cells were selected with 2 μg/mL puromycin for 5 days. Cells were plated in 96-well plates at 50,000 cells/well and stimulated with 500 ng/mL doxycycline and 500 nM Shield1, or left untreated (‘none’) for 6 days. On day 6, cells were collected and stained for receptor knockout analysis by flow cytometry. The lentiviral sgRNA transduced Jurkats were stained with PE anti-human CD28 antibody (1:100), or FITC anti-human CD71 (1:25). Non-targeting control Jurkat cells were used for positive control receptor stain and isotype controls to determine positive and negative receptor gates.
Gene editing activity of Strict-R Inducible Hygromycin-Cas9 Lentiviral System in A549 cells after induction with doxycycline + Shield1 for 72 hours

A549 were transduced with Dharmacon™ Strict-R™ Inducible Cas9 Lentiviral System with hygromycin resistance. After 14 days of hygromycin selection cells were transduced at an MOI of 0.3 with Edit-R pre-designed lentiviral sgRNA targeting PPIB positive control (VSGH12671), CD71/TFRC (VSGH12605-257052386) or CD58/LAF-3 (VSGH12605-256231081). Cells were selected for an additional 5 days with 2 μg/mL puromycin in TET-system approved A549 medium. For the gene editing experiment, double-selected A549 cell lines were plated in a 96-well plate at 20,000 cells/well in duplicate per induction condition: 500 ng/mL doxycycline + 500 nM Shield1, 500 ng/mL doxycycline alone, 500 nM Shield1 alone or no supplement to A549 medium (none). Cells were collected and lysed at 72 hours post induction to isolate genomic DNA for DNA mismatch detection assay with T7EI and Sanger sequencing with TIDE analysis. A. Gel electrophoresis (with FastRuler Low Range DNA Ladder) of T7EI endonuclease digested PCR products corresponding to gene target in A549. Below, in bar graph, is the quantification of T7EI gene editing by mismatch assay using the T7EI calculator. B. Quantification of gene editing by tracking of indels by decomposition (TIDE) analysis.
Robust gene editing and minimal leakiness with Dharmacon™ Strict-R™ Inducible Cas9 Lentiviral System in two cancer cell lines
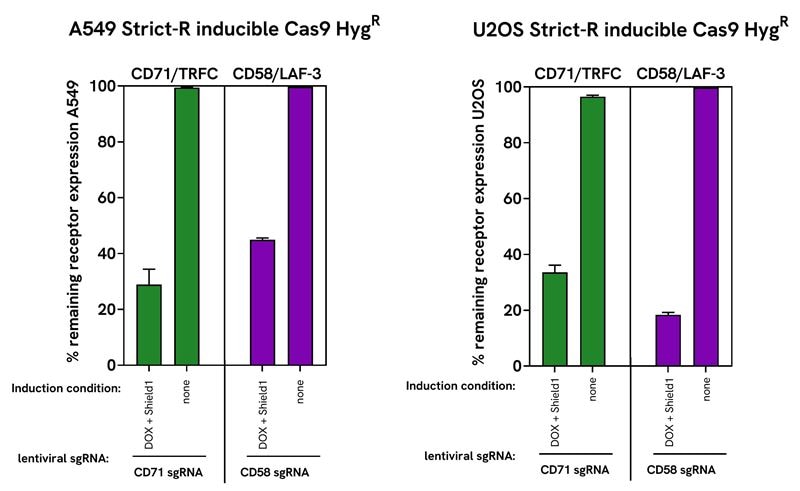
A549 were transduced with Dharmacon™ Strict-R™ inducible Cas9 lentiviral system with hygromycin resistance. After 14 days of hygromycin selection cells were transduced at an MOI of 0.3 with Edit-R pre-designed lentiviral sgRNA targeting PPIB positive control (VSGH12671), CD71/TFRC (VSGH12605-257052386) or CD58/LAF-3 (VSGH12605-256231081). Cells were selected for an additional 5 days with 2 μg/mL puromycin in TET-system approved A549 medium. For the gene editing experiment, double-selected A549 cell lines were plated in a 96-well plate at 20,000 cells/well in duplicate per induction condition: 500 ng/mL doxycycline + 500 nM Shield1, 500 ng/mL doxycycline alone, 500 nM Shield1 alone or no supplement to A549 medium (none). Cells were collected and lysed at 72 hours post induction to isolate genomic DNA for DNA mismatch detection assay with T7EI and Sanger sequencing with TIDE analysis. A. Gel electrophoresis (with FastRuler Low Range DNA Ladder) of T7EI endonuclease digested PCR products corresponding to gene target in A549. Below, in bar graph, is the quantification of T7EI gene editing by mismatch assay using the T7EI calculator. B. Quantification of gene editing by tracking of indels by decomposition (TIDE) analysis
- D. Bhaya, et al. CRISPR-Cas systems in bacteria and archaea: versatile small RNAs for adaptive defense and regulation. Annu. Rev. Genet.45, 273-297 (2011).
- M. Jinek, et al. A Programmable Dual-RNA-Guided DNA Endonuclease in Adaptive Bacterial Immunity. Science337, 816-821 (2012).
- E. Deltcheva, et al. CRISPR RNA maturation by trans-encoded small RNA and host factor Nuclease III. Nature471, 602-607 (2011).
- P. Mali, et al. RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science339, 823-826 (2013).
- Y. Fu, et al. High-frequency off-target mutagenesis induced by CRISPR-Cas nucleases in human cells. Nat. Biotechnol.31, 822-826 (2013).
- P.D. Hsu, et al. DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nat. Biotechnol.31, 827-832 (2013).
- T. Wang et al. Genetic screens in human cells using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Science343, 80-84 (2014).
- D.Y. Guschin, et al. A rapid and general assay for monitoring endogenous gene modification. Methods Mol. Biol.649, 247-256 (2010).
- L.Cong, et al. Multiplex Genome Engineering Using CRISPR/Cas Systems. Science339, 819-823 (2013).
- J.C. Kappes, X. Wu and J.K. Wakefield. Production of trans-lentiviral vector with predictable safety. Methods Mol. Med.76, 449-465 (2003).
- R.H. Kutner, X.-Y. Zhang and J. Reiser. Production, concentration and titration of pseudotyped HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors. Nat. Protoc.4, 495-505 (2009)
- Anaszynski, Laura A et al., A rapid, reversible, and tunable method to regulate protein function in living cells using synthetic small molecules. Cell. 126, 995-1004 (2006).
- Egeler, Emily L et al., Ligand-switchable substrates for a ubiquitin-proteasome system. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 286, 31328-36 (2011).
- Maynard-Smith, Lystranne A et al., A directed approach for engineering conditional protein stability using biologically silent small molecules. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 282, 24866-72 (2007).
LentiBOOST Lentivirus Transduction Enhancer is a uniquely formulated transduction reagent that can be used with or without lentivirus spinfection in order to increase successful viral transduction events while preserving cell viability. Especially critical for preserving precious primary cells from patient cohorts, or, for engineering complex animal models; improving transduction efficiency can save time and costs by increasing the success of each editing/transduction step, or, even avoid the loss of irreplaceable samples. Additionally, LentiBOOST technology is already used in the manufacturing of a number of clinical stage therapies providing the opportunity to demonstrate improved workflow applicability to the clinic.
LentiBOOST can be purchased through the Dharmacon Reagents catalog.
To learn more about LentiBOOST technology visit the Revvity LentiBOOST webpage.
Supporting Data
Improved CD8+ T-cell SMARTvector™ shRNA lentiviral system transduction using LentiBOOST™ Lentivirus Transduction Enhancer
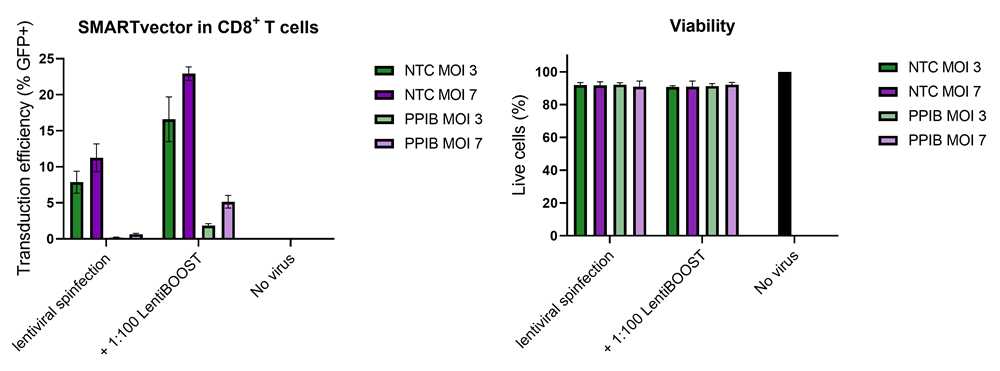
100,000 primary human CD8+ T cells were transduced with either 30,000 (MOI 3, green) or 70,000 (MOI 7, purple) TUs of SMARTVector™ mCMV tGFP Lentiviral Control Particles targeting either NTC or PPIB along with 1:100 LentiBOOST transduction enhancer. Cells were centrifuged at 800 x g for one hour at 32 °C followed by a four hour incubation prior to removal of lentiviral particles and transduction enhancer. Transduction efficiency (%GFP+ out of live cells) and viability were determined 5 days post-transduction by flow cytometry. The addition of LentiBOOST technology markedly improved transduction efficiencies without significantly impacting cell viability.
Improved CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell Edit-R™ All-in-one sgRNA/Cas9 lentiviral system transduction using LentiBOOST™ Lentivirus Transduction Enhancer
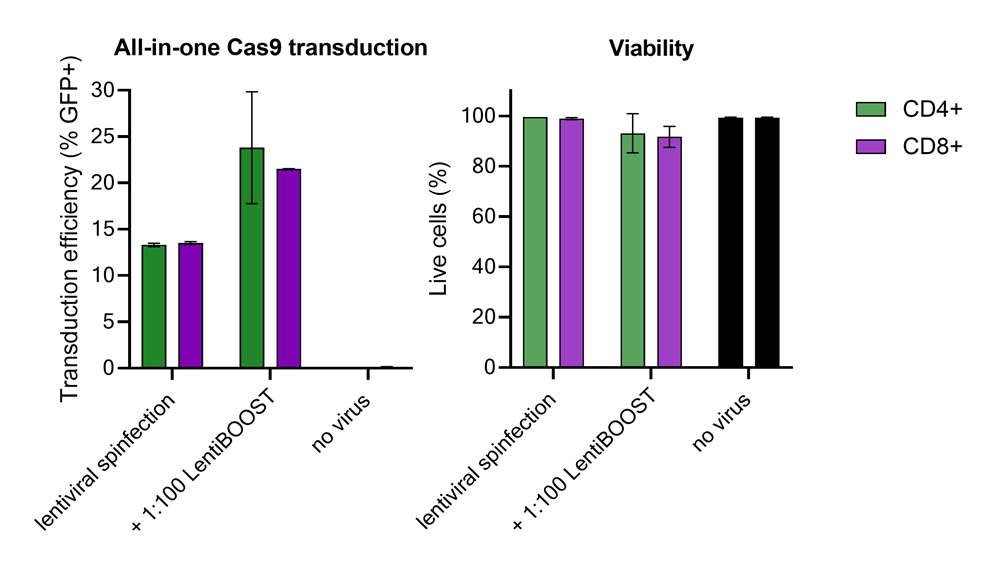
100,000 primary human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from two donors were transduced with 250,000 TUs of Edit-R GFP Delivery controls mCMV along with 1:100 LentiBOOST transduction enhancer. Cells were centrifuged at 800 x g for one hour at 32 °C followed by an overnight incubation prior to removal of lentiviral particles and transduction enhancer. Transduction efficiency and viability were determined 72 hours post-transduction by flow cytometry. The addition of LentiBOOST technology markedly improved transduction efficiencies without significantly impacting cell viability.
Improved transduction of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) with the Strict-R™ Inducible CRISPRa lentiviral system transduction using LentiBOOST™ Lentivirus Transduction Enhancer

10,000 WTC hiPS cells were transduced with either 20,000 (MOI 2, green) or 40,000 (MOI 4, purple) TUs of Strict-R™ Inducible EGFP dCas9-VPR Lentiviral Particles along with 1:100 LentiBOOST transduction enhancer. Cells were centrifuged at 800 x g for one hour at 32 °C followed by an overnight incubation prior to removal of lentiviral particles and transduction enhancer. Transduction efficiency and viability were determined 72 hours post-transduction by flow cytometry. The addition of LentiBOOST markedly improved transduction efficiencies without significantly impacting cell viability.
Related Products
Single guide RNA expressing vectors for effective and accurate gene knockout
Synthetic guide RNAs for efficient gene knockout and unparalleled specificity
Perform unbiased, phenotypic knockout screens without the need for costly infrastructure
LentiBOOST transduction enhancer can increase successful viral transduction in challenging to transduce cells, or, complex cellular engineering work; while preserving cell viability and minimizing the amount of viral particles required for your experiment. LentiBOOST technology is actively used in the production of clinical stage lentivirally delivered therapies, including some approved therapies, providing a direct path to therapeutic applicability for your research studies. Tested with Dharmacon Lentiviral reagents.
