- Gene editing
- Gene editing reagents
- Edit-R Predesigned synthetic crRNA
Edit-R predesigned crRNA
Synthetic guide RNAs for efficient gene knockout & unparalleled specificity
- Guaranteed to edit the target gene of interest
- Designed to maximize the likelihood of functional protein knockout and minimize off-target editing
- Transfection-ready RNAs eliminate cloning and in vitro transcription steps
- Chemically modified for improved nuclease resistance
- New! Edit-R human sgRNA designs have been updated to the latest RefSeq as of August 22, 2025.
Reminder: Synthetic crRNA must be paired with synthetic tracrRNA to form the full guide RNA complex that targets Cas9 editing.

Edit-R Predesigned synthetic crRNA
1Start Here
2Choose
Functional and specific targeting for high-confidence gene knockout results
Edit-R crRNA is a chemically synthesized RNA, comprised of 20 nucleotides identical to the genomic DNA target site, followed by the required S. pyogenes repeat sequence. Complexing crRNA with tracrRNA is required to complete the full ~100mer guide RNA structure needed for genomic editing. Therefore when ordering synthetic crRNA, be sure to include tracrRNA with it.
While CRISPR-Cas9 is a highly effective tool for interrogating gene function, not all guide RNAs are effective in attaining functional protein knockout. To address this problem, Horizon developed an algorithm that is trained to select guides that give the highest likelihood of generating a functional gene knockout, not just creating an insertion or deletion.

New! Edit-R human crRNA designs have been updated to the latest RefSeq in 2025 providing the most specific and genomically relevant guides for producing efficient protein knockout. This allows the Edit-R algorithm to target the latest genome annotations more accurately and efficiently providing you with the best solution for your research needs. Please reach out to Scientific Support if you have any questions or read our blog on revvity.com.
All guide RNA designs are top algorithm picks for each gene; qualitative ranks for functionality and specificity allow you to fine tune human guide RNA choice to your specific application. The functionality score is a predicted indication of how likely this guide is to produce a functional knockout. The specificity score is based on the predicted risk of cutting activity at potential off-target sites. To learn more, visit our algorithm for Edit-R guide RNA page.
Chemical modifications are applied to all predesigned crRNAs to resist degradation by nucleases to improve performance in applications using co-delivery with DNA-free Cas9. Learn more in this featured article.
Required components for an Edit-R CRISPR-Cas9 gene engineering experiment using synthetic crRNA:
- A source of Cas9 nuclease - in protein, mRNA, or lentiviral vector format.
- Edit-R CRISPR RNA (crRNA) designed to target the gene of interest
- Edit-R trans-activating CRISPR RNA (tracrRNA)
The Edit-R Predesigned Guide RNA Guarantee
We guarantee that EVERY predesigned guide RNAs will provide successful editing at the target site when delivered as described in the Edit-R Technical Manuals.
The Edit-R guide RNA guarantee is valid when used with any wild type S. pyogenes Cas9 nuclease, including mRNA, expression plasmid, protein, or stable Cas9 expression, and Edit-R crRNAs must be used with Edit-R tracrRNA for the guarantee to apply.
Analysis of editing of the treated cell population must be shown using a T7EI or Surveyor mismatch detection assay. If successful editing is not observed for a predesigned Edit-R guide RNA while an appropriate side-by-side Edit-R positive control is successful, a one-time replacement of a different predesigned Edit-R guide RNA of the same format and quantity will be provided at no cost.
A replacement will only be approved upon discussion with our Scientific Support team.
Successful editing at the DNA level does not always lead to functional gene knockout; it is recommended to test multiple guide RNAs to determine the most effective guide RNA for knockout of your target gene.
This guarantee does not extend to any accompanying experimental costs, does not apply to guide RNAs ordered via the CRISPR Design Tool, and will not be extended to the replacement guide RNA.
Gene knockout workflow using Cas9 nuclease mRNA and synthetic sgRNA or crRNA:tracrRNA
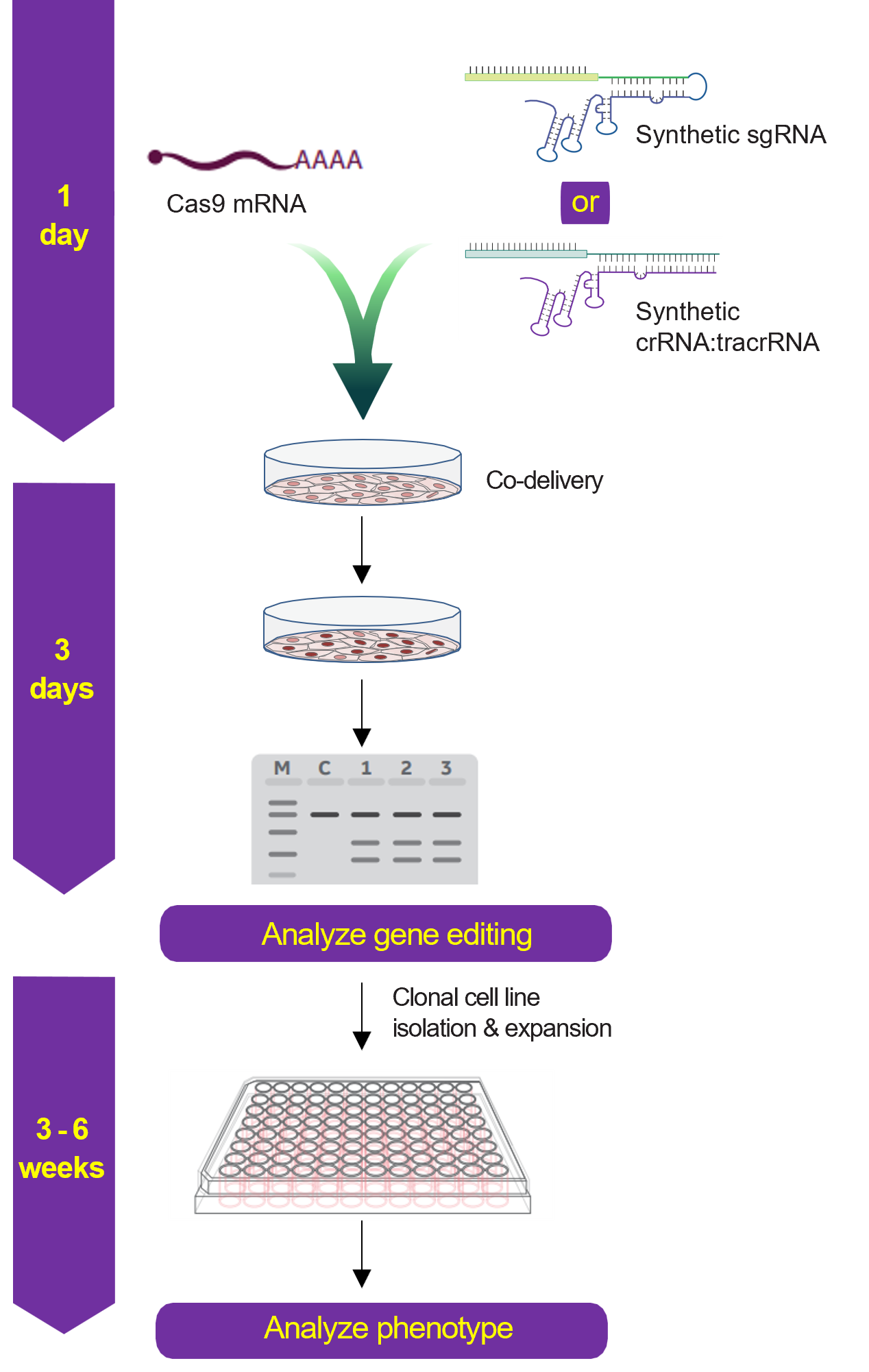
Gene knockout workflow using Cas9 nuclease protein and synthetic sgRNA or crRNA:tracrRNA

Gene knockout workflow using lentiviral Cas9 expression particles and synthetic sgRNA or crRNA:tracrRNA

Edit-R synthetic crRNA controls
-
Positive controls and detection primers
Species-specific crRNAs targeting well-characterized genes, as well as mismatch detection assay primers, to determine the effectiveness of your gene editing conditions for maximal efficiency.
-
Non-targeting controls
Non-targeting controls to evaluate cellular responses to CRISPR-Cas9 components in the absence of gene target-specific crRNA.
-
Cutting controls
Cutting control (safe harbor) crRNAs recommended for determination of baseline cellular responses in CRISPR-Cas9 experiments.
Synthetic guide RNA
-
Edit-R tracrRNA
Edit-R trans-activating CRISPR RNA (tracrRNA) is synthetic, HPLC-purified, long RNA required for use with Edit-R crRNA to form the complex that programs Cas9 nuclease. It is modified for nuclease resistance and can be used with modified or unmodified Edit-R crRNA.
-
Edit-R synthetic positive crRNA controls and detection primers
Species-specific crRNAs targeting well-characterized genes, as well as mismatch detection assay primers, to determine the effectiveness of your gene editing conditions for maximal efficiency.
-
Edit-R synthetic crRNA non-targeting controls
Non-targeting controls to evaluate cellular responses to CRISPR-Cas9 components in the absence of gene target-specific crRNA.
-
CRISPR design tool
Place a custom guide RNA order, or design and order your own synthetic sgRNA, crRNA, or lentiviral sgRNA with our easy-to-use interface.
-
Cherry-pick libraries
Have a favorite gene list? Customize and order plates of predesigned crRNA for knockout studies in your targets of interest
Cas9 nuclease
-
Cas9 nuclease protein NLS
Purified Cas9 protein ready to use for DNA-free nuclease expression.
-
Cas9 nuclease mRNA
Purified Cas9 mRNA for transient Cas9 Nuclease expression. Fluorescent options available for sorting, enrichment and visualization of delivery.
-
Lentiviral Cas9 nuclease expression reagents
Purified lentiviral particles or plasmid DNA for generation of stable Cas9 nuclease-expressing cell populations. Constitutive or inducible promoter options are available.
Synthetic crRNA editing efficiency
Functional protein knockout of VCP is observed in a cell-based assay using stably-expressed Cas9 and Edit-R synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA in a recombinant U2OS line.
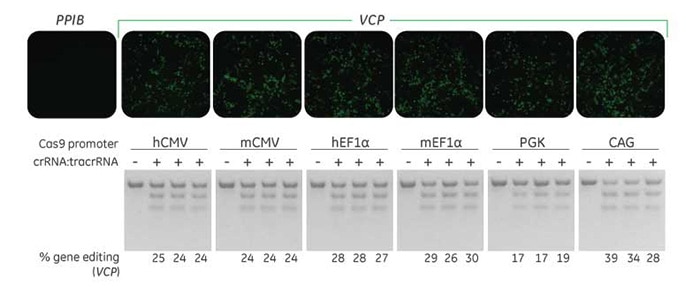
A recombinant U2OS ubiquitin-EGFP proteasome cell line (Ubi[G76V]-EGFP) was stably transduced with blasticidin-resistant, Cas9 expressing lentiviral particles under the control of the indicated promoters. A population of cells with stably integrated Cas9-BlastR was selected with blasticidin-treatment for a minimum of 10 days before transfections. Cells were transfected with 50 nM Edit-R synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA complex targeting VCP, a gene required for proteasome function, using DharmaFECT 3 Transfection Reagent. After 72 hours, transfected cells were examined for EGFP+ cells (upper panel) and the relative frequency of gene editing was calculated (lower panel) based on a DNA mismatch detection assay with T7 Endonuclease I.
Knockout performance of synthetic sgRNA and crRNA:tracrRNA
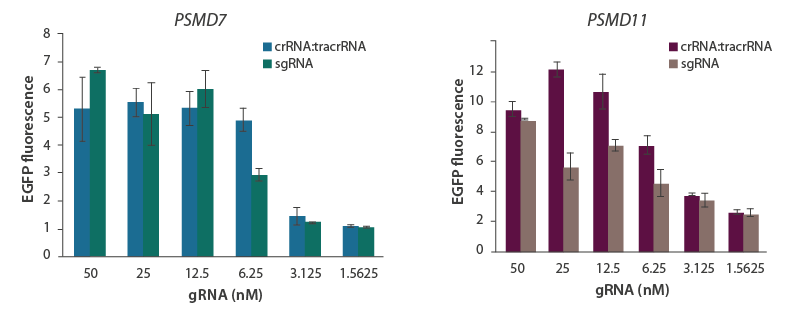
A U2OS ubiquitin-EGFP cell line stably expressing Cas9 under a CAG promoter was transfected with decreasing concentrations of guide RNA (either crRNA:tracrRNA or sgRNA) targeting proteasome components PSMD7 (A) or PSMD11 (B). Transfected cells were assessed for functional gene knockout through EGFP accumulation/intensity.
Synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA is compatible with all Cas9 Nuclease formats
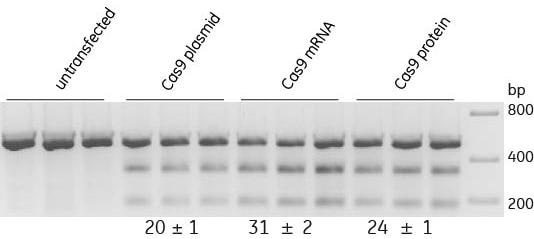
U2OS cells were plated at 10,000 cells/well one day prior to transfection. Cells were transfected with either Edit-R Cas9 Nuclease plasmid (200 ng), Edit-R Cas9 Nuclease mRNA(200 ng) or Cas9 nuclease protein (25 nM) and crRNA:tracrRNA (25 nM) targeting PPIB using DharmaFECT Duo transfection reagent (0.4 uL/well) in biological triplicates.
Efficient gene editing in Cas9-expressing NIH/3T3 cell lines by transfection with Edit-R crRNA:tracrRNA
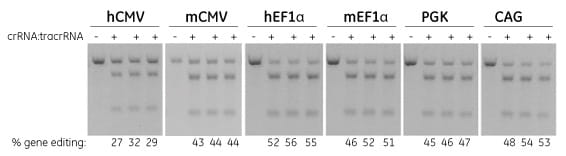
NIH/3T3 cells were stably transduced with lentiviral particles containing Cas9 and a blasticidin resistance gene driven by the indicated promoters. A population of stably integrated cells were selected with blasticidin for a minimum of 10 days before transfections. Cells were transfected with 50 nM Edit-R synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA targeting PPIB using DharmaFECT 1 transfection reagent. After 72 hours, the relative frequency of gene editing was calculated based on a DNA mismatch detection assay with T7 Endonuclease I.
Design algorithm performance
crRNA with high scores from the Edit-R algorithm have higher cleavage efficiency than low-scoring designs
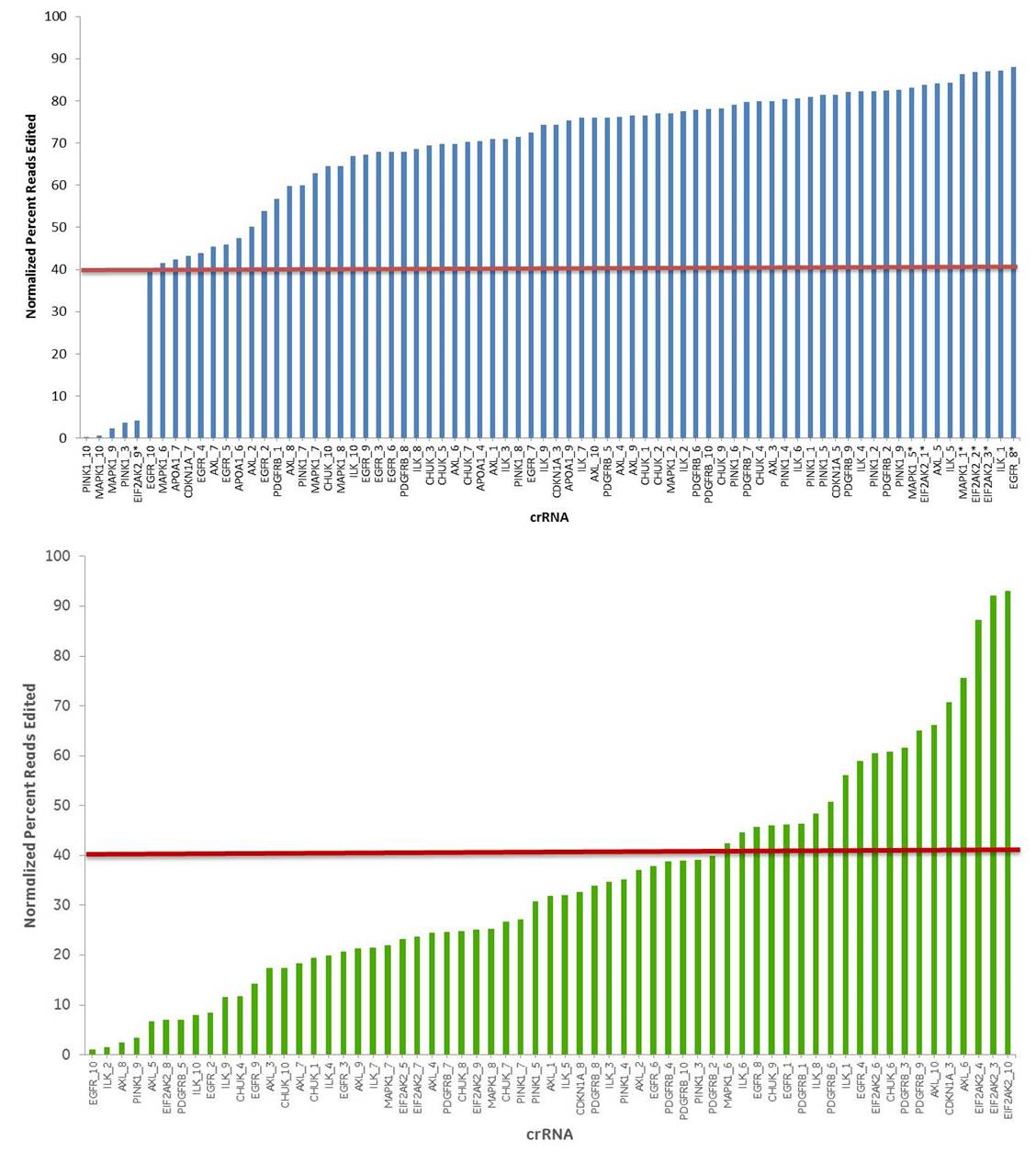
10 crRNAs with high functional scores for 10 genes (blue bars) and 10 crRNAs with low functional scores for the same genes (yellow bars) were tested for editing by NGS. 93% of the high-scoring crRNAs and 32 % of the low scoring crRNAs showed > 40% of editing (indel formation). The Cas9-HEK293T cell line was transfected with 50 nM crRNA:tracrRNA, using 0.25 µL/well of DharmaFECT 1. 72 hours post-transfection, cells were lysed and Nextera transposon-adapted amplicons spanning each crRNA site were generated for every treated sample as well as for a matched control amplicon from untransfected samples. Samples were indexed using the Nextera 96-well index kit and pooled for sequencing on a MiSeq instrument. Reads that passed NGS quality filtering criteria were aligned to the reference file (Bowtie2 v2.1.0). Percent perfect reads were calculated and normalized to the control untransfected samples (Samtools v0.1.12a); the data is presented as normalized percent edited.
crRNAs with high functional scores from the Edit-R algorithm show stronger phenotypes in ApoONE assay than low-scoring designs
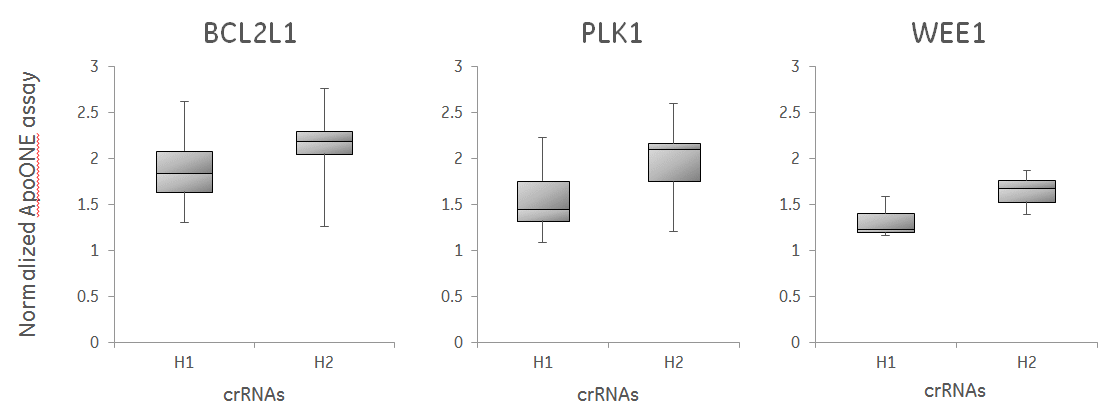
U2OS-Proteasome cells with integrated Cas9 (under CAG promoter) were plated in 96-well plates at 10,000 cells per well. 24 hours after plating, cells were transfected with 25 nM crRNA:tracrRNA using 0.2 µg/well of DharmaFECT4. Cell were analyzed for apoptosis 48 hours after transfection using the ApoONE homogeneous assay (Promega). For the box plot, the crRNAs were divided into bottom half (h2) and top half (h4) based on their Edit-R algorithm functional score (110 total data points represented). The medians, distribution of data between the lower and upper halves and the minimum and maximum values demonstrate that high-scoring crRNAs have increased functionality.
Designs with gaps & mismatches can cause off-target cleavage
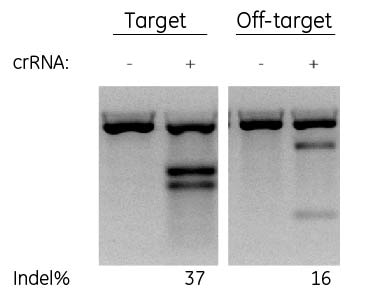
T7EI mismatch analysis for a crRNA showing the intended target site (GGTCATCTGGGAGAAAAGCG) and a predicted off-target site that was identified by the Edit-R alignment tool but no other online tool, containing one gap and one mismatch (GGT-ATCTGGGAGAAAAGCa) Many commonly used web-based crRNA specificity tools do not fully account for gaps when performing alignments.
crRNA modification designs
Efficiency of gene editing with 2x MS modified or unmodified crRNA:tracrRNA
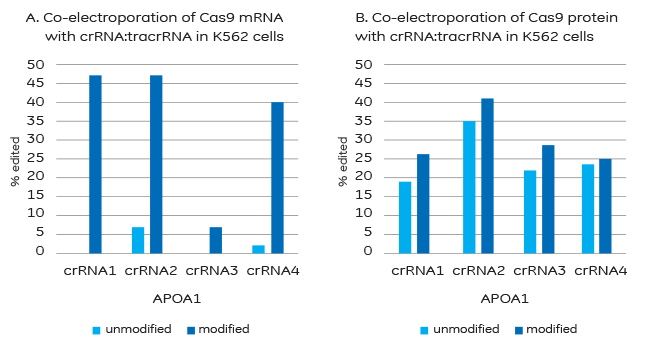
A. Modifications to block degradation by nucleases are required for successful co-electroporation of Cas9 mRNA and crRNA:tracrRNA. B. Co-electroporation of Cas9 protein and crRNA:tracrRNA does not require stabilizing modifications, but results may be improved with their addition.
Edit-R synthetic guide RNAs cause virtually no innate immune response or toxicity compared to in vitro transcribed guide RNA
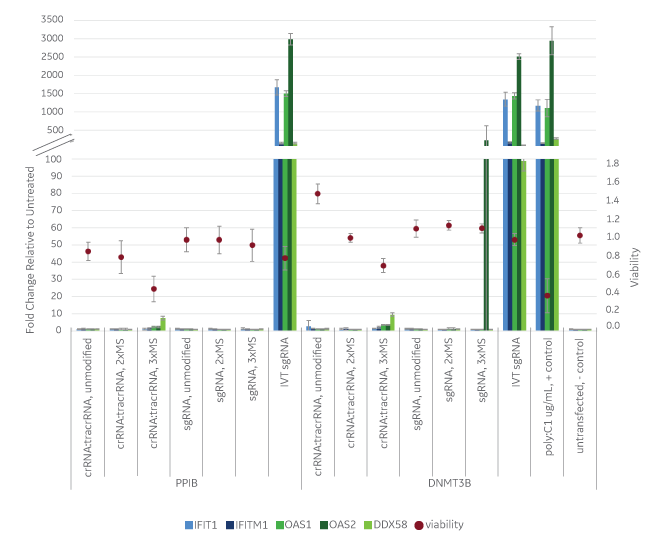
A HEK293T Cas9 nuclease expressing cell line was transfected with different synthetic guide RNA formats including unmodified crRNA:tracrRNA, crRNA:tracrRNA modified with 2xMS on 5’ crRNA and 3’ tracrRNA, crRNA:tracrRNA modified with 3xMS on both 5’ and 3’ crRNA and tracrRNA, unmodified synthetic sgRNA, modified synthetic sgRNA with 5’ and 3’ 2xMS or 3xMS, and in vitro transcribed (IVT) sgRNA targeting PPIB and DNMT3B genes. At 72 hours viability was assessed with the Resazurin reduction assay (red dots) and the levels of five immune response genes were quantified by RT-qPCR. MS = 2’-O-methyl nucleotides and phosphorothioate backbone linkages.
Position and structure of modifications for improved nuclease resistance on Edit-R synthetic crRNA and tracrRNA
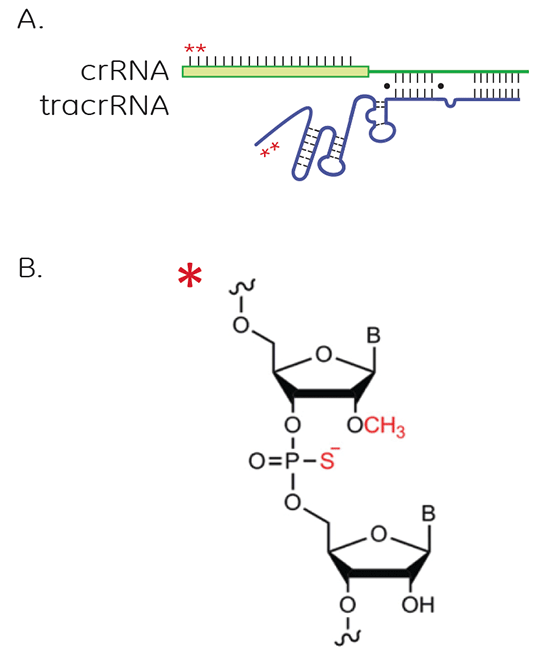
A. Position of modifications for nuclease resistance on Edit-R synthetic crRNA and tracrRNA. Edit-R synthetic guide RNAs contain 2ʹ-O-methyl (2ʹ-OMe) and backbone phosphorothioate linkages (PS) on the two nucleotides at the 5ʹ end of the crRNA (green strand) and on the two nucleotides at the 3’ end of the tracrRNA (blue strand). B. Structure of the 2ʹ-OMe and PS backbone phosphorothioate linkages.
How much crRNA and tracrRNA do I need?
This table provides the approximate number of experiments that can be carried out for lipid transfection methods at the recommended crRNA:tracrRNA working concentration (25 nM:25nM) in various plate/well formats. Calculations do not account for pipetting errors.
| crRNA nmol | tracrRNA nmol | 96-well plate 100 µL reaction volume | 24-well plate 500 µL reaction volume | 12-well plate 1000 µL reaction volume | 6-well plate 2500 µL reaction volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 | 800 | 160 | 80 | 32 |
| 5 | 5 | 2000 | 400 | 200 | 80 |
| 10 | 10 | 4000 | 800 | 400 | 160 |
| 20 | 20 | 8000 | 1600 | 800 | 320 |
- R. Barrangou, A. Birmingham, et. al. Advances in CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering: lessons learned from RNA interference. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(7) 3407-3419 (2015)
- M.L. Kelley, Ž. Strezoska, et al. Versatility of chemically synthesized guide RNAs for CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing. J. Biotechnol. 233, 74–83 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.06.011
- Basila, M., M. L. Kelley, et al.. Minimal 2’-O-methyl phosphorothioate linkage modification pattern of synthetic guide RNAs for increased stability and efficient CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing avoiding cellular toxicity. PLoS One. 12, e0188593 (2017). doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188593
- Anderson, E.M., A. Haupt, et al. Systematic analysis of CRISPR-Cas9 mismatch tolerance reveals low levels of off-target activity. J. Biotechnol. 211, 56-65 (2015)
Application notes
-
A CRISPR-Cas9 gene engineering workflow: generating functional knockouts using Edit-R Cas9 and synthetic crRNA and tracrRNA - Application Note
-
CRISPR gene editing and transcriptional activation in human iPS cells - Application Note
-
Homology-directed repair with Dharmacon Edit-R CRISPR-Cas9 reagents and single-strand DNA oligos - Application Note
-
Microinjection of zebrafish embryos using Dharmacon Edit-R Cas9 Nuclease mRNA, synthetic crRNA, and tracrRNA for genome engineering - Application Note
-
Optimization of reverse transfection of Edit-R synthetic crRNA and tracrRNA components with DharmaFECT transfection reagent in a Cas9-expressing cell line - Application Note
Posters
-
2'-O-methyl phosphorothioate linkage-modified synthetic guide RNAs for efficient CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing and reduced cellular toxicity - Poster
-
A Synthetic CRISPR-Cas9 System for Homology-Directed Repair - Poster
-
An algorithm for selecting functional and specific CRISPR-Cas9 guide RNAs - Poster
-
An algorithm for selecting highly functional and specific guide RNAs for CRISPR-Cas9 gene knockout - Poster
-
Chemical modifications of synthetic guide RNA for enhanced RNA stability and reduced cellular toxicity in CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing - Poster
-
Complete alignment identification of CRISPR-Cas9 genomic off-targets using Edit-R CRISPR specificity tool - Poster
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing utilizing chemically synthesized RNA - Poster
-
CRISPR-mediated transcriptional activation and simultaneous gene knockout and activation with synthetic guide RNAs
-
Homology-directed repair with Edit-R CRISPR-Cas9 and single-strand DNA oligos - Poster
-
Increasing gene editing efficiencies in eukaryotic cell lines by selection of appropriate CRISPR-Cas9 reagents - Poster
-
Simultaneous gene knockout and transcriptional activation using S. pyogenes VPR-Cas9 mRNA
Product data
Protocols
-
10 mM Tris-HCl buffer pH 7.4 - Protocol
-
Cas9 Nuclease mRNA Electroporation - Protocol
-
Cas9 nuclease protein electroporation - Protocol
-
Fluorescent Cas9 Nuclease mRNA for enrichment of transfected cells - Protocol
-
Synthetic guide RNA resuspension - Protocol
-
T7E1, TIDE, and NGS analysis protocol for Dharmacon™ Edit-R™ gene editing experiments
Quick protocols
Safety data sheets
Selection guides
Technical manuals
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering with Cas9 nuclease expression plasmids and Edit-R synthetic RNA - Technical Manual
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering with Cas9 nuclease mRNA and Edit-R synthetic RNA - Technical Manual
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering with Cas9 nuclease protein and Edit-R synthetic guide RNA - Technical Manual
-
CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering with lentiviral Cas9 particles and Edit-R synthetic guide RNA - Technical Manual
Related Products
Chemically synthesized trans-activating CRISPR RNA required for use with synthetic crRNA for fast and easy gene editing
A DNA-free option for Cas9 nuclease expression. Purified Cas9 nuclease protein with an enhanced hybrid NLS composition enabling more efficient nuclear delivery and gene editing. Suitable for a wide range of RNP workflows including nucleofection or co-transfection with Edit-R synthetic guide RNA for a completely DNA-free genome engineering system.
Purified Cas9 nuclease mRNA for co-transfection with synthetic guide RNA for a completely DNA-free genome engineering system
Choose from a range of popular cell line backgrounds, then simply deliver your CRISPR guide RNA for straightforward gene knockout
