The presence of off-target effects can greatly complicate the interpretation of experimental data. Dharmacon™ ON-TARGETplus™ siRNAs and CRISPRmod CRISPRi system are designed to knock down the target gene with minimal off-target effects and are powerful tools for orthogonal validation strategies resulting in highly specific readouts.
Researchers are aware of off-target effects caused by an introduction of unnatural components into the cell. However, those can be minimized and there are various strategies to distinguish them from a true phenotype.
RNAi has a broad spectrum of applications in single assay as well as in screening formats. It has been extensively characterized and optimized by us for decades. Recently, the Dharmacon product family has expanded to include novel CRISPRmod CRISPRi technology reagents, targeting specific locations and blocking transcription without cutting the DNA. This opens another door for target specific knockdown at the transcriptional DNA level, in addition to RNAi reagents controlling the mRNA expression level and thereby preventing translation.
As we recommend orthogonal validation strategies regarding multiple cellular expression machineries, the combined usage of specific gene silencing methods provides a profound hit validation.
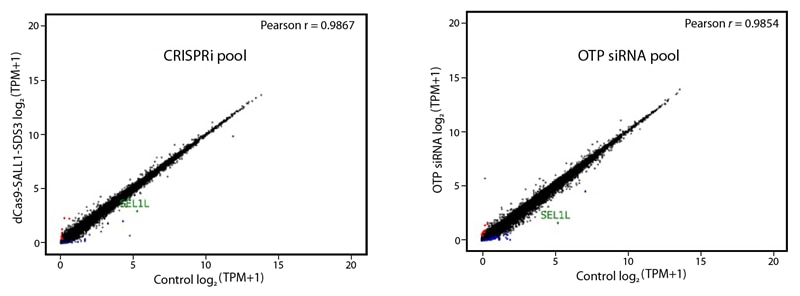
Addressing the specificity of both techniques, we have performed a comparative off-target signature gene expression analysis of our novel CRISPRmod CRISPRi and well known ON-TARGETplus reagents by targeting SEL1 in USOS cells. The gene expression levels (log2TPM, Transcripts Per Million) of SEL1 knockdown was measured and compared to respective non-targeting controls.
Despite the differences in the mode of action in both techniques, our CRISPRi and RNAi reagents measurements turned out being highly specific as shown by remarkably Pearson´s correlation coefficients in both gene expression signatures (Figure 1).
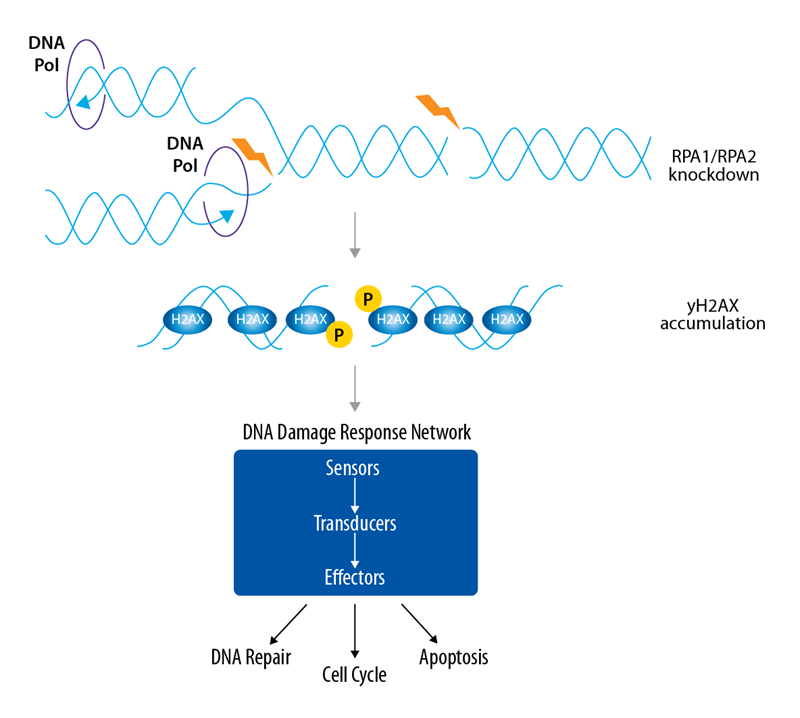
Based on this, we have performed a companion DNA Damage Response Assay suggesting that both methods can also be used for orthogonal validation steps. Replication protein A (RPA) consists of RPA1, RPA2, and RPA3 subunits, described to have a high binding affinity to single-stranded DNA and fulfilling key regulatory functions in the DNA damage response1,2 (Figure 2).
As expected, the knockdown of RPA1 and RPA2 resulted in an accumulation of unrepaired double strand DNA breaks, which can be monitored via an increased phosphorylated H2AX level (γ-h2AX). Both gene modulation tools showed confirming results in comparison of respective wild-type controls (Figure 3).
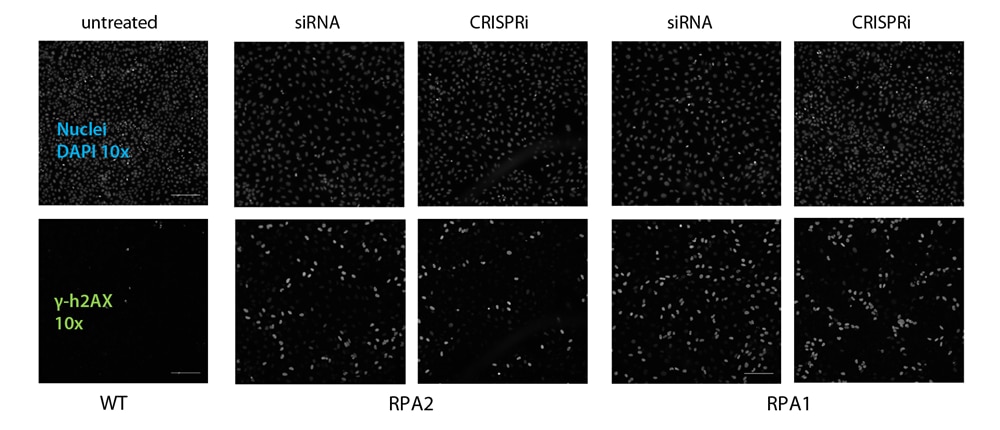
These results corroborate the specificity of both gene modulation techniques by targeted repression of DNA transcription (CRISPRi) and mRNA translation (RNAi). Conclusively, the expression of functional proteins can be down-regulated from multiple angles, leading to high- confidence datasets.
We offer a broad spectrum of our novel CRISPRi reagents besides our widely used RNAi reagents. Horizon´s Scientific Support is a team made up of trained scientists supporting gene editing and gene modulation technologies. We’re happy to discuss your project in English, French, German, Italian, or Spanish; and have teams in both the US and Europe to provide flexible service hours.
CRISPRi resources
Welcome to the toolbox, CRISPRi - Blog article
CRISPR-mediated transcriptional repression with a novel dCAS9 fusion protein and synthetic guide RNAs - Poster
RNAi resources
Reducing off-target effects in RNA interference experiments – Blog article
Ensure success with appropriate controls in your RNAi experiments – Blog article
siRNA screening: development of hit stratification strategies - Poster
Off-target effects: disturbing the silence of RNA interference (RNAi) – Application note
Dharmacon publications (see RNAi specificity & functionality) – Recommended Reading
