Homology-directed repair (HDR) relies on the presence of a donor template with sufficient homology to the regions flanking the cut site. The length of the homology arms and the type of donor (ssDNA oligo or plasmid) will depend on the type and size of precise modification being made. Figure 1 illustrates the use of a donor oligo for insertion of a short DNA region, such as a tag or a restriction site. Go to the Edit-R HDR Donor Designer to see how easy it is to customize a donor oligo!
Donor oligo for precise insertion of a short DNA sequence
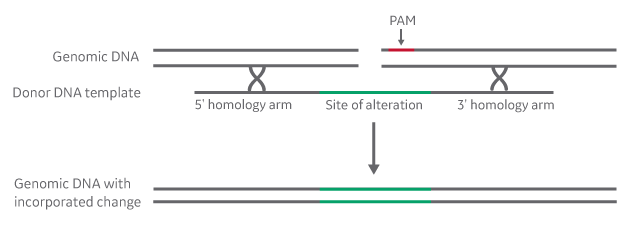
Figure 1. For larger insertions, such as a fluorescent marker, a donor plasmid template is required, with appropriately longer homology arms to support efficient recombination. The Edit-R HDR DNA Plasmid donor kit along with the Edit-R HDR Donor Designer make the process of designing and assembling a donor plasmid quick and straightforward.
Donor plasmid assembly for insertion of a fluorescence selection marker
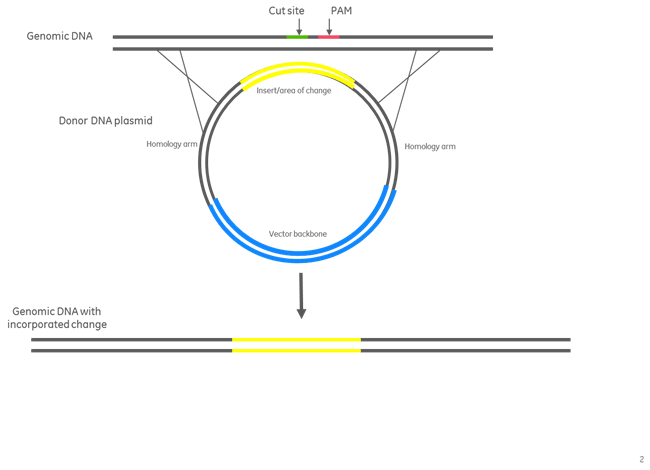 Figure 2. Donor plasmid assembly for insertion of a fluorescent marker
Figure 2. Donor plasmid assembly for insertion of a fluorescent marker
Diagram of the plasmid donor cloning workflow
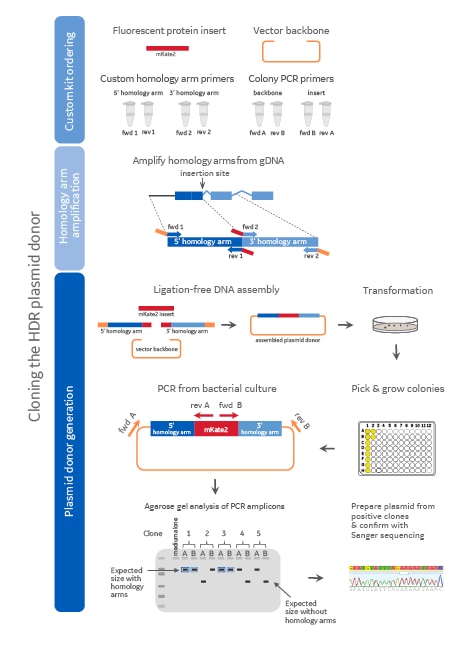
Diagram of the plasmid donor cloning workflow including component ordering, homology arm amplification, and plasmid donor generation. Colors on the diagram indicate the origin of the DNA (dark blue = 5' homology arm, light blue = 3' homology arm, red = mKate2 fluorescent reporter sequence, orange = plasmid backbone). medium alone = media-only negative PCR control.
Donor DNA oligo concentration optimization
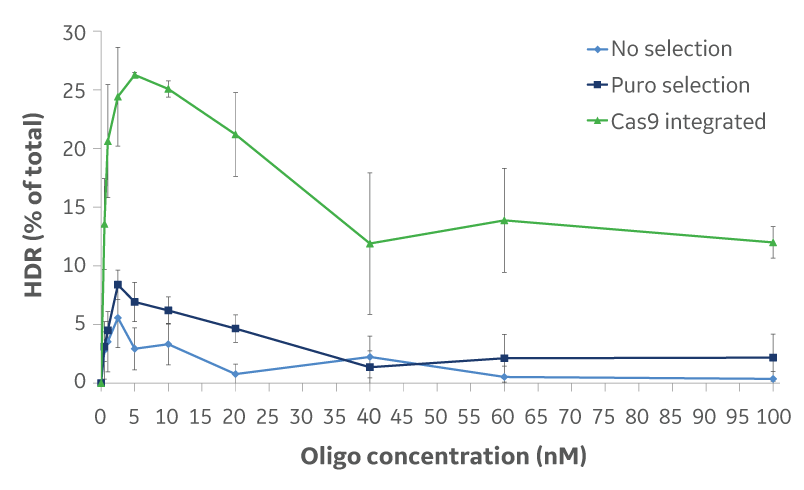
DharmaFECT Duo Transfection Reagent was used to co-transfect U2OS cells with a Cas9 expression plasmid, EMX1 crRNA:tracrRNA, and increasing concentrations of a donor DNA oligo with 30 nucleotide homology arms. Alternatively, a Cas9-integrated U2OS cell line was transfected with crRNA:tracrRNA to target EMX1, and increasing concentrations of a donor DNA oligo with 30 nucleotide homology arms. The RFLP assay was used to determine the amount of HDR knockin for each concentration of donor DNA oligo in each transfection. Data presented is from three independent transfections.
Optimizing homology arm length for maximal HDR knockin
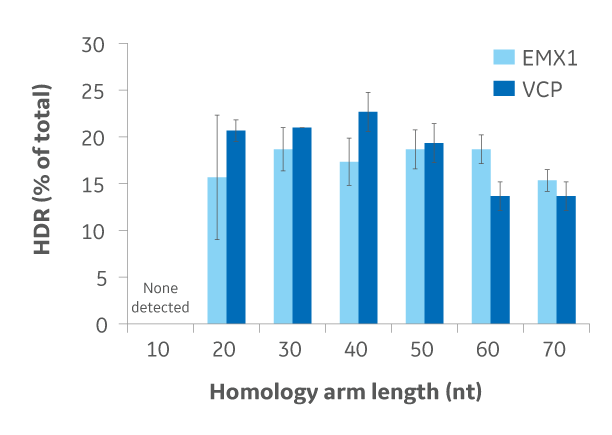
DharmaFECT Duo Transfection Reagent was used to transfect a Cas9integrated U2OS cell line with crRNA:tracrRNA targeting EMX1 or VCP and a donor DNA oligo. Different donor DNA oligos were used, each with increasing homology arm length. A RFLP assay was performed on three independent transfections to determine HDR-based knockin for each donor DNA oligo with different homology arm lengths.
Gene editing at the VCP locus
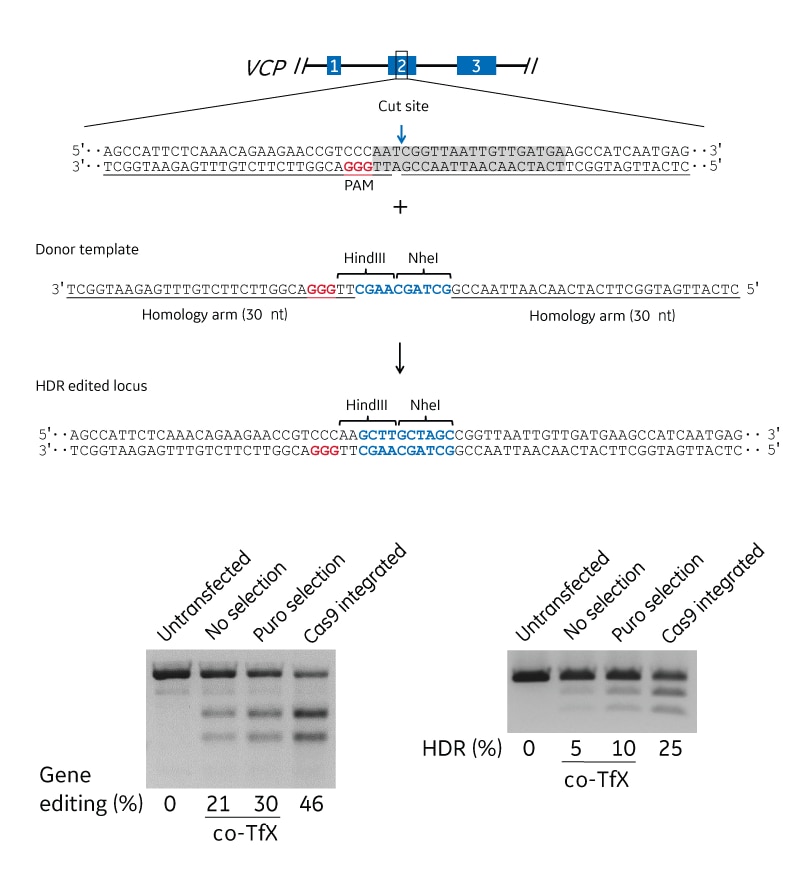
Expressed Cas9 and synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA were used to target the VCP locus for HDR genome engineering in U2OS cells. A. Schematic of the VCP locus. Exons are indicated by the blue boxes. The guide sequence in the synthetic crRNA is indicated by the gray highlighted region, the PAM is indicated in red, and the cut site is indicated by the blue arrow. The inserted sequence is indicated in blue. B. Analysis of the efficiency of indel mutations using mismatch detection analysis of untransfected cells and transfected cells without (no selection) and with (puro selection) puromycin selection or using a Cas9-expressing cell line (Cas9 integrated). The percent editing is indicated below the gels. C. Analysis of the efficiency of HDR-based insertion of a HindIII and NheI restriction enzyme sites introduced using a 30 nucleotide homology arm DNA oligo. Percent HDR editing was calculated using an RFLP assay with NheI digestion of VCP PCR amplicons. co-Tfx = co-transfection.
Gene editing at the EMX1 locus
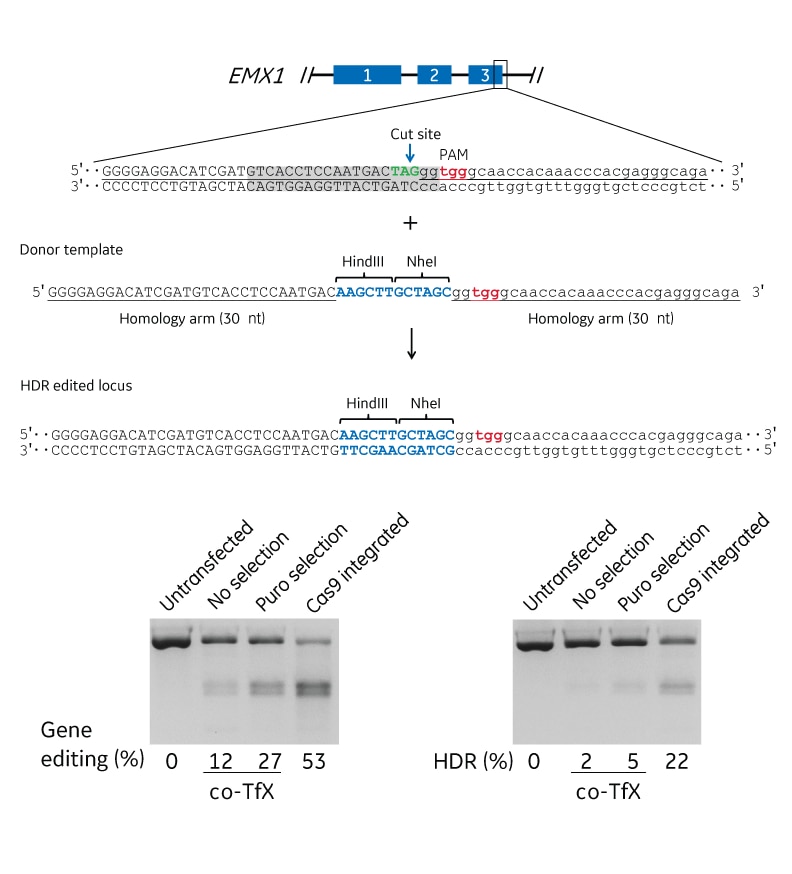
Expressed Cas9 and synthetic crRNA:tracrRNA were used to target the EMX1 locus for HDR genome engineering in U2OS cells. A. Schematic of the EMX1 locus. Exons are indicated by the blue boxes and uppercase lettering; introns are indicated by the lowercase lettering. The guide sequence in the crRNA is indicated by the gray highlighted region, the PAM is indicated in red, and the cut site is indicated by the blue arrow. The inserted sequence is indicated in blue, and the endogenous stop codon is green. B. Analysis of the efficiency of indel mutations using mismatch detection analysis of untransfected cells and transfected cells without (no selection) and with (puro selection) puromycin selection or using a Cas9expressing cell line (Cas9 integrated). The percent editing is indicated below the gels. C. Analysis of the efficiency of HDR insertion of a HindIII and NheI restriction enzyme sites introduced using a 30 nucleotide homology arm DNA oligo. Percent HDR editing was calculated using an RFLP assay with NheI digestion of EMX1 PCR amplicons. co-Tfx = co-transfection.

 Figure 2. Donor plasmid assembly for insertion of a fluorescent marker
Figure 2. Donor plasmid assembly for insertion of a fluorescent marker




